(1.广东海洋大学 水产学院,广东 湛江 524088;2.广东粤海饲料集团股份有限公司,广东 湛江 524000;3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(湛江),广东 湛江 524025)
石斑鱼Epinephelu作为中国四大海水养殖品种之一,养殖产量仅次于大黄鱼Larimichthys crocea [1],在海水养殖中占据重要地位。但是,随着养殖规模的不断扩大,水环境、养殖管理及饲料等因素易导致石斑鱼黏膜受损,如体表黏膜受损感染哈维氏弧菌Vibrio harveyi后出现皮肤溃疡,肠道黏膜受损产生肠炎,从而降低养殖产量,造成经济损失[2]。肠炎作为石斑鱼的一种常见病,虽非严重疾病,但由于肠道黏膜屏障损伤使机体防御能力下降会引起众多并发症。肠道物理屏障是肠黏膜屏障中最重要的一环,主要由肠上皮细胞与相邻细胞间的连接蛋白构成,包括紧密连接(tight junctions,TJ)、缝隙连接、黏附连接及桥粒。TJ位于连接复合体最顶端,是维持肠黏膜物理屏障的结构基础,其调控水、离子和小分子溶质等物质经旁细胞途径的转运,是决定细胞间通透性的关键因素[3]。
TJ蛋白分为跨膜蛋白(Claudins家族、Occludin与Tricellulin等膜相关结构域蛋白家族和连接黏附分子家族)和胞浆蛋白(ZO家族、扣带素和丝状肌动蛋白结合蛋白等)。其中,Claudins蛋白家族是构成紧密连接的主要骨架蛋白,不仅可以调节细胞旁通透性,还参与机体抵抗病原体感染、促进器官发育和缺氧应激反应相关的生物学过程[4]。Claudins家族基因的分布具有明显的组织特异性,且在不同鱼类的组织分布中存在一定的差异。鲤Cyprinus carpio肠道和肝脏均可高表达Claudin-3b和Claudin-3c亚型[5],但鲑Oncorhynchus keta肠道却不表达Claudin-3b,肝脏也不表达Claudin-3c[6]。值得关注的是,这种组织或细胞特异性表达模式与各Claudin分子所发挥的作用特点有关,有助于机体适应不同组织或不同部位的需要从而维持生理稳态。
Claudins家族基因在饲粮因素的影响下可对肠道屏障发挥重要的调控作用。霉菌毒素可以通过降低特定亚型Claudin-3和Claudin-4的表达量破坏结肠癌细胞(Caco-2)的物理屏障性能[7]。海藻多糖可促进猪小肠上皮细胞紧密连接蛋白基因Claudin-1的表达,并且通过下调NF-κB炎症信号通路相关基因表达维持上皮屏障功能,可有效预防肠道炎症的发生[8]。饲粮中的大豆球蛋白会显著降低草鱼Ctenopharyngodon idellus后肠Claudin-3c基因的表达[9],而适量的谷氨酸则可通过上调建鲤C.carpio var Jian肠道Claudin-2、Claudin-3和Claudin-7基因的表达,维护肠道物理屏障[10]。精氨酸对肠细胞的增殖分化和维持细胞形态结构具有重要的保护作用,适量精氨酸可显著上调草鱼肠道Claudin c、Claudin-15a、Claudin-12和Claudin-3基因的表达水平[11]。本研究团队前期通过石斑鱼肠道染色切片(H.E),观察到适量精氨酸可改善石斑鱼肠道皱襞高度和肌层厚度[12]。本研究中,克隆和分析了珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀×E.lanceolatus♂Claudin-3与Claudin-12的基因序列,并通过饲料精氨酸调控观测两基因在石斑鱼肠道的表达丰度,评价Claudin-3与Claudin-12在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼生长和肠道黏膜屏障中的作用,以期为石斑鱼健康养殖提供科学参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
试验用珍珠龙胆石斑鱼幼鱼购自广东省湛江市东南码头石斑鱼苗场。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 试验设计
1)基因克隆及表达。挑选15尾体态健康、规格一致的石斑鱼幼鱼(初始体质量11.0 g±0.5 g),试验设置3组,每组5尾,采用丁香酚麻醉后,于冰盘上解剖取其脑、鳃、皮肤、肌肉、肝脏、胃、前肠、中肠、后肠、头肾、体肾、脾和心脏等13个组织,置于装有RNAlater (Invitrogen 公司)的冻存管内,投入液氮中速冻后移至-80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存备用。
2)精氨酸干预试验。结合本团队前期研究基础[12],设置3组分别含有1.96%、3.06%和3.74%精氨酸的等氮等脂试验饲粮(表1)。每个处理设置3个平行,每个平行放养30尾珍珠龙胆石斑鱼(初始体质量为20.79 g±0.09 g)。每日8:00和17:00投喂两次,饱食投喂8周。试验用水为经过沉淀、沙滤的天然海水,养殖期间水温为(29±1)℃,盐度为25,自然光照,持续供氧,溶解氧≥5 mg/L,养殖水体中氨氮含量≤0.03 mg/L。
表1 基础饲料及营养成分组成
Tab.1 Ingredients and nutrient composition in basic diet
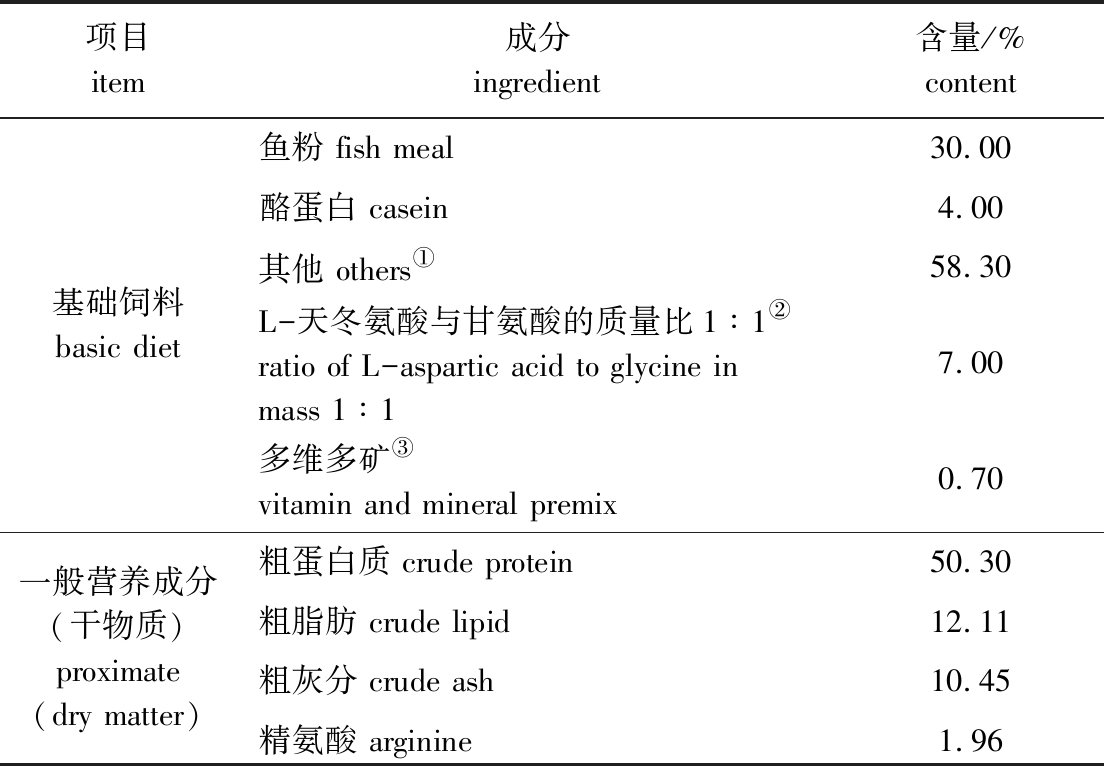
项目item成分ingredient含量/%content基础饲料basic diet鱼粉 fish meal30.00酪蛋白 casein4.00其他 others①58.30L-天冬氨酸与甘氨酸的质量比1∶1②ratio of L-aspartic acid to glycine in mass 1∶17.00多维多矿③vitamin and mineral premix0.70一般营养成分(干物质)proximate(dry matter)粗蛋白质 crude protein50.30粗脂肪 crude lipid12.11粗灰分 crude ash10.45精氨酸 arginine1.96
注:① 其他(%):豆粕18,面粉16.21,玉米蛋白粉10,必需氨基酸4.31,鱼油3,豆油3,卵磷脂1.5,磷酸二氢钙1.6,氯化胆碱0.5,甜菜碱0.1,维生素C 0.05,乙氧基喹啉0.03;② 通过依次降低各组非必需氨基酸的含量(7.00%、5.90%、5.22%),添加精氨酸(0%、1.10%、1.78%),使得各试验组精氨酸含量分别为1.96%、3.06%、3.74%;③ 多维多矿由青岛玛斯特生物技术有限公司惠赠。
Note:① other(%):soybean meal 18,wheat meal 16.21,corn gluten meal 10,essential amino acids 4.31,fish oil 3,soybean oil 3,lecithin 1.5,calcium biphosphate 1.6,choline chloride 0.5,betaine 0.1,vitamin C 0.05,ethoxy quinoline 0.03;② arginine is added(0%,1.10% and 1.78%)by adjusting the content of nonessential amino acids to balance the diets(7.00%,5.90% and 5.22%),the content of arginine in each experimental group is 1.96%,3.06% and 3.74%,respectively;③ vitamin and mineral premix,a gift from Qingdao Master Biotechnology Company Limited.
养殖试验结束后,将每个平行的鱼进行称重和计数,用于计算增重率和成活率。从每个平行随机取3尾鱼,剥离肠道取其中段,放入无酶冻存管中,立即投入液氮中速冻,随后转移到-80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存,用于分析精氨酸对Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因mRNA表达的影响。
1.2.2 总RNA提取与逆转录 用Trizol试剂(Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,USA)提取各组织总RNA。通过10 g/L琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA的完整性,并用紫外分光光度法(OD260 nm/OD280 nm)对RNA纯度进行评估后,进行反转录(Revert Aid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit,Fermentas公司)。
1.2.3 Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因克隆 根据NCBI提供的金头鲷Sparus aurata、多刺棘光鳃鲷Acanthochromis polyacanthus、高体鰤Seriola dumerili、贝氏隆头鱼Labrus bergylta、大刺鳅Mastacembelus armatus等近缘物种的参考序列,采用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计3条特异性5′RACE引物和2条特异性3′RACE引物(引物均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成)。使用Super Script Ⅱ RT 酶和引物GSP-1 对总RNA进行目的基因第一链cDNA合成,使用RNase Mix 对合成的cDNA进行去RNA处理。使用GLASSMAX DNA isolation spin cartridges对经RNAase处理过的cDNA进行纯化。PCR扩增反应:95 ℃下预变性4 min;94 ℃下循环变性30 s,62 ℃下退火复性30 s,72 ℃下延伸1 min,共进行34个循环;最后在72 ℃下再延伸10 min,4 ℃下保存。PCR产物采用15 g/L琼脂糖凝胶进行检测,目的片段用琼脂糖凝胶回收,将PCR回收产物与pMD18T克隆载体进行连接,转化到DH-5A感受态细胞后获得阳性克隆,送至生工生物工程(上海)有限公司进行测序。
1.2.4 实时定量PCR 13个组织及精氨酸干预试验的肠道组织总RNA经反转录后,进行实时荧光定量(TaKaRa SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM Ⅱ Kit),反应体系为20 μL。qRT-PCR扩增反应:95 ℃下预变性30 s;95 ℃下循环变性15 s,58 ℃下退火复性34 s,72 ℃下延伸20 s,共进行40个循环。之后进行熔解曲线分析,结果以β-actin为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因的相对表达量,实时定量引物见表2。
表2 基因克隆和实时定量引物序列
Tab.2 Sequences of primers for gene cloning and quantitative PCR
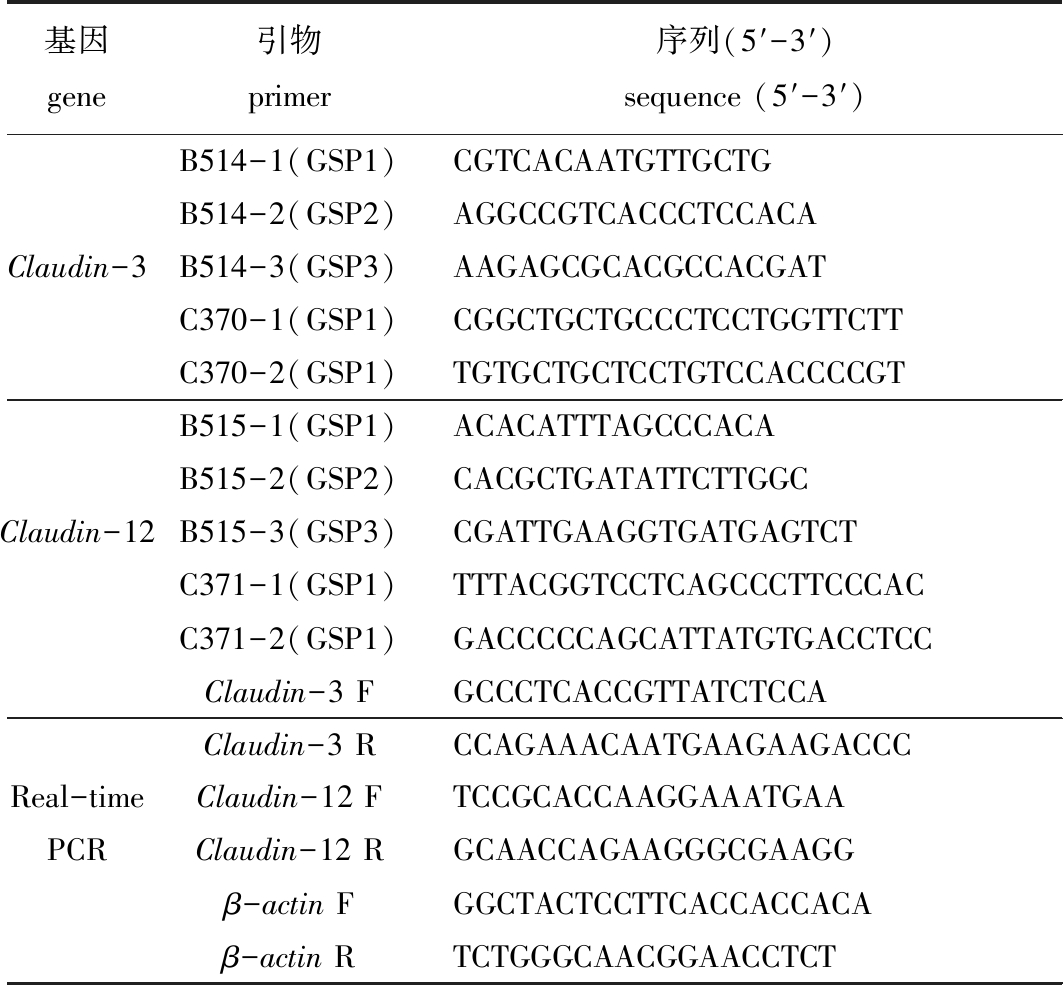
基因gene引物primer序列(5′-3′)sequence (5′-3′)B514-1(GSP1)CGTCACAATGTTGCTGB514-2(GSP2)AGGCCGTCACCCTCCACAClaudin-3B514-3(GSP3)AAGAGCGCACGCCACGATC370-1(GSP1)CGGCTGCTGCCCTCCTGGTTCTTC370-2(GSP1)TGTGCTGCTCCTGTCCACCCCGTB515-1(GSP1)ACACATTTAGCCCACAB515-2(GSP2)CACGCTGATATTCTTGGCClaudin-12B515-3(GSP3)CGATTGAAGGTGATGAGTCTC371-1(GSP1)TTTACGGTCCTCAGCCCTTCCCACC371-2(GSP1)GACCCCCAGCATTATGTGACCTCCClaudin-3 FGCCCTCACCGTTATCTCCAClaudin-3 RCCAGAAACAATGAAGAAGACCCReal-time Claudin-12 FTCCGCACCAAGGAAATGAAPCRClaudin-12 RGCAACCAGAAGGGCGAAGGβ-actin FGGCTACTCCTTCACCACCACAβ-actin RTCTGGGCAACGGAACCTCT
1.2.5 序列比对与系统发育分析 使用ORF查找器(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)预测Claudin-3和Claudin-12氨基酸序列的OFR。使用SMART程序(http://smart.embl.de/)和Signal P软件(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/signal p/)预测蛋白质结构域和信号肽。使用DNAMAN 6.0对Claudin-3与Claudin-12的氨基酸多重序列进行比对,并利用MEGA 5.0软件基于邻接法构建氨基酸序列的系统发生进化树。
1.2.6 指标计算 增重率(%)和成活率(%)的计算公式为
增重率=(末均质量-初均质量)/初均质量×
100%,
成活率=终末鱼体数量/初始鱼体数量×100%。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据均以平均值±标准误(mean±S.E.)表示,采用SPSS 20.0软件进行单因素方差分析(ANOVA),采用Tukey法进行多重比较,显著性水平设为0.05。
2 结果与分析
2.1 Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因克隆与序列分析
珍珠龙胆石斑鱼的Claudin-3 cDNA全长序列为1 544 bp,包括一个153 bp的5′UTR和743 bp的3′UTR,ORF为648 bp,可编码215个氨基酸的蛋白,预测该蛋白的相对分子质量为23 100;使用SMART程序和Signal P软件预测Claudin-3蛋白具有4个跨膜结构域,无信号肽(图1(a))。
珍珠龙胆石斑鱼的Claudin-12 cDNA全长序列为1 236 bp,包括一个118 bp的5′UTR和92 bp的3′UTR,ORF为1 026 bp,可编码341个氨基酸的蛋白,预测该蛋白的相对分子质量为37 400;使用SMART程序和Signal P软件预测Claudin-12蛋白具有3个跨膜结构域,无信号肽(图1(b))。
2.2 Claudin-3和Claudin-12氨基酸序列比对与系统发育分析
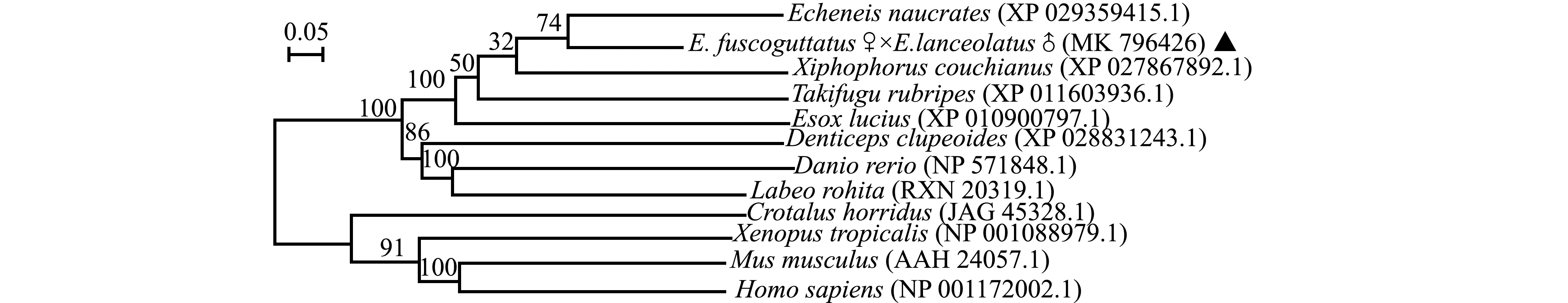
采用DNAMAN Package 6.0软件进行氨基酸多序列比对,用MEGA 5.0采用邻接法分别构建Claudin-3和Claudin-12氨基酸序列的分子系统发育树,结果如图2~图5所示。
珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-3与斜带石斑鱼Epinephelus coioides首先聚为一支,亲缘关系最近,二者的同源性也最高,一致性高达98.14%,然后与高体鰤汇为一支,与两栖类的爪蟾Xenopus tropicalis、哺乳动物的人Homo sapiens聚为不同分支,亲缘关系较远,同源性也较低(图2、图3、表3);珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-12首先与 Echeneis naucrates聚为一支,二者的同源性也最高,一致性高达91.79%,然后与库舍剑尾鱼Xiphophorus couchianus汇为一支,与两栖类的爪蟾、爬行类的森林响尾蛇Crotalus horridus和哺乳类的小鼠Mus musculus等物种的亲缘关系较远,同源性也较低(图4、图5、表3)。
Echeneis naucrates聚为一支,二者的同源性也最高,一致性高达91.79%,然后与库舍剑尾鱼Xiphophorus couchianus汇为一支,与两栖类的爪蟾、爬行类的森林响尾蛇Crotalus horridus和哺乳类的小鼠Mus musculus等物种的亲缘关系较远,同源性也较低(图4、图5、表3)。
表3 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-3与Claudin-12氨基酸序列与其他物种的同源性比对
Tab.3 Homology comparison of amino acid sequences of Claudin-3 and Claudin-12 in hybrid grouper E.fuscoguttatus ♀ E.lanceolatus♂with other species

物种speciesGenBank accession number 一致性/%identifyClaudin-3斜带石斑鱼Epinephelus coioidesACH73085.198.14金头鲷Sparus aurataAHY19850.197.67高体鰤Seriola dumeriliXP 022594248.197.21大黄鱼Larimichthys croceaXP 019126959.196.81斑马鱼Danio rerioNP 571842.171.63斑点叉尾鮰Ictalurus punctatusNP 001188045.170.37爪蟾Xenopus tropicalisNP 001005709.172.56鸡Gallus gallusNP 989533.170.23牦牛Bos grunniensASR74724.166.82人Homo sapiensNP 001297.165.91Claudin-12 Echeneis naucratusXP 029359415.191.79红鳍东方鲀Takifugu rubripesXP 011603936.186.22库舍剑尾鱼Xiphophorus couchianusXP 027867892.185.04白斑狗鱼Esox luciusXP 010900797.181.38露斯塔野鲮Labeo rohitaRXN20319.170.89斑马鱼Danio rerioNP 571848.170.32齿鲱Denticeps clupeoidesXP 028831243.169.34森林响尾蛇Crotalus horridusJAG45328.148.92爪蟾Xenopus tropicalisNP 001188045.147.96小鼠Mus musculusAAH24057.150.93人Homo sapiensNP 001297.151.52
2.3 Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因的组织表达
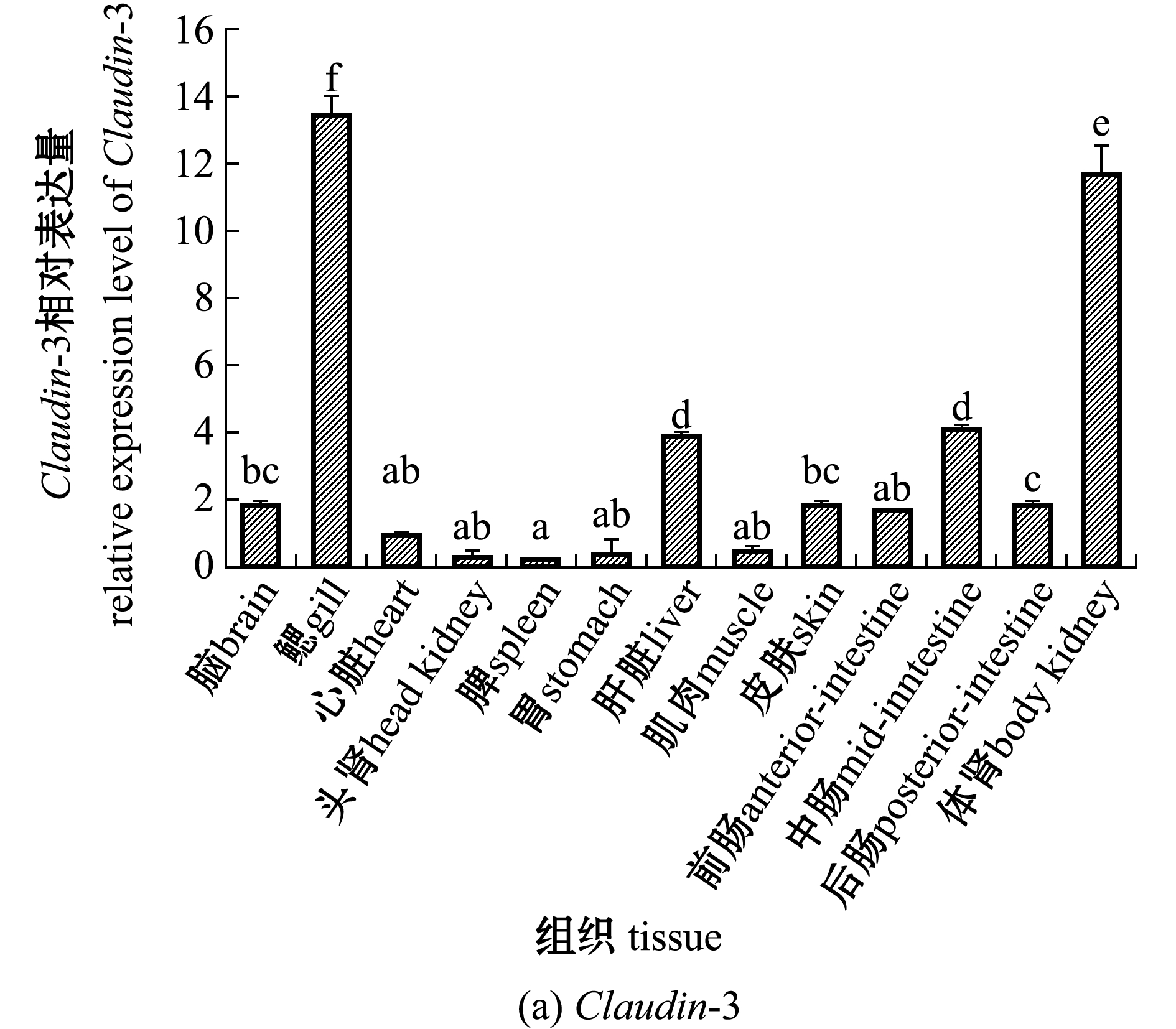
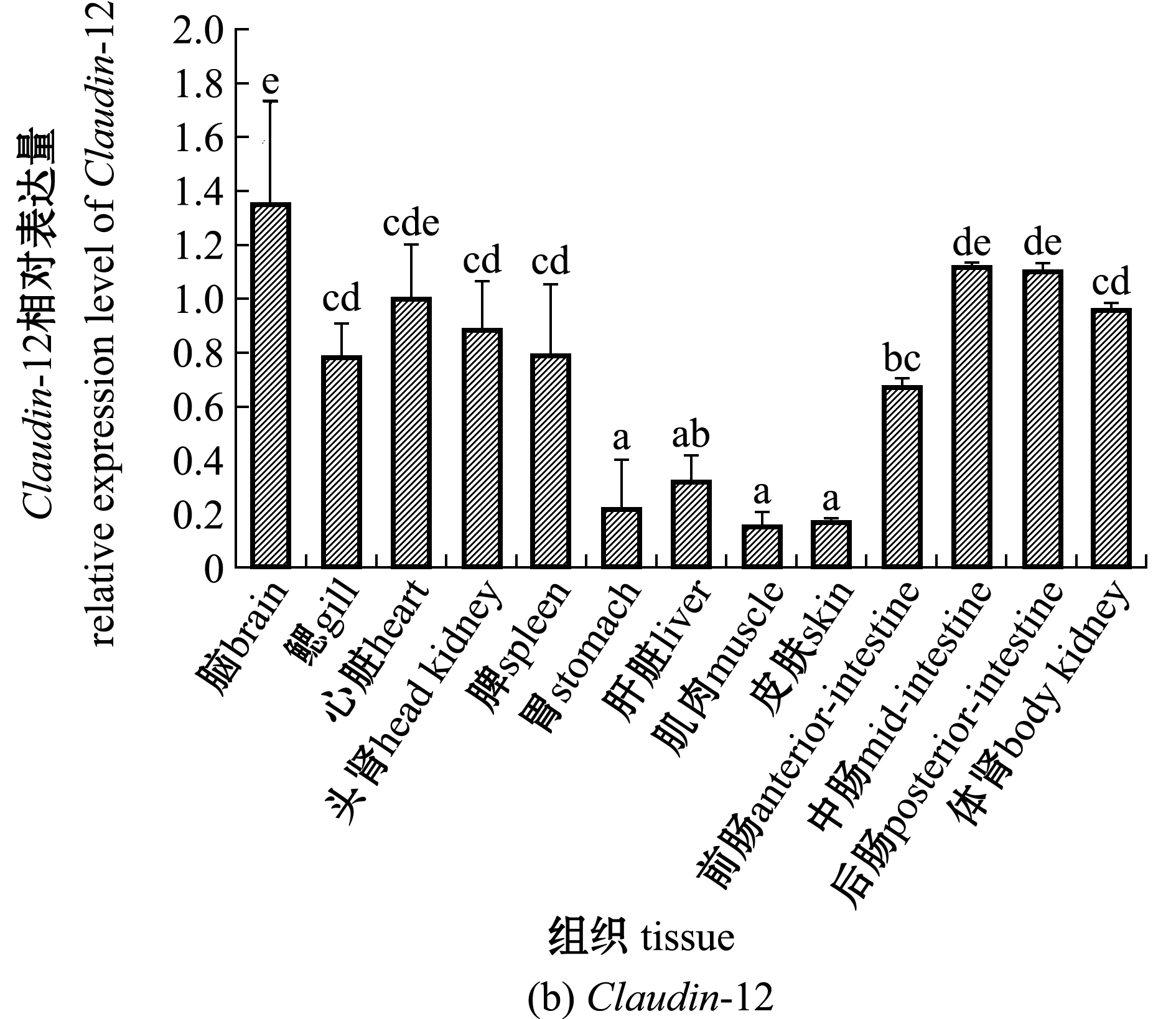
从图6可见:Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼的13种组织中均有表达;Claudin-3基因在鳃和体肾中的表达量显著高于其他组织(P<0.05),在中肠和肝脏中的基因表达量显著高于其余9个组织(P<0.05),其余9个组织中Claudin-3基因表达量相对较低;Claudin-12基因在脑中的表达量最高,与中肠、后肠和心脏相比无显著性差异(P>0.05),但显著高于其他组织(P<0.05),鳃、体肾、头肾、脾中的Claudin-12基因表达量显著高于胃、肝脏、肌肉和皮肤(P<0.05),且这4个组织间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
2.4 饲料中精氨酸对石斑鱼生长和存活的影响
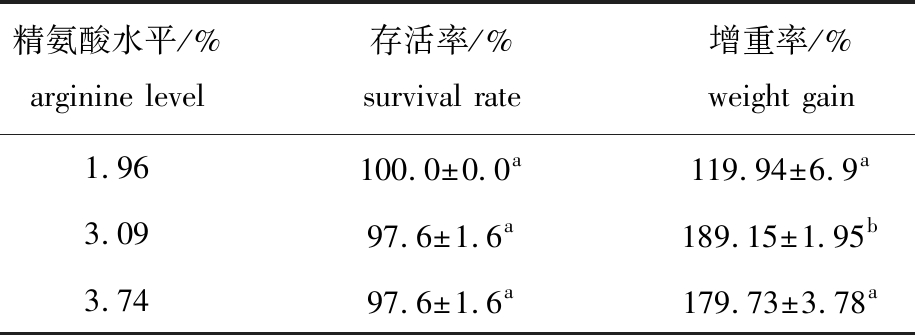
从表4可见:饲料中的精氨酸水平对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼存活率无显著性影响(P>0.05);3.06%精氨酸组石斑鱼的增重率最高,较1.96%组显著高出69.21%(P<0.05),较3.74%组显著高出9.42%(P<0.05),但1.96%精氨酸组与3.74%精氨酸组鱼体增重率无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
表4 饲料中精氨酸水平对石斑鱼存活率和增重率的影响
Tab.4 Effects of dietary arginine levels on survival and weight gain of hybrid grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀×E.lanceolatus♂
精氨酸水平/%arginine level存活率/%survival rate增重率/%weight gain1.96100.0±0.0a119.94±6.9a3.0997.6±1.6a189.15±1.95b3.7497.6±1.6a179.73±3.78a
注:同列中标有不同字母者表示组间有显著性差异(P<0.05),标有相同字母者表示组间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
Note:The means with different letters within the same column are significantly different in the groups at the 0.05 probability level,and the means with the same letter within the same column are not significant differences.
2.5 精氨酸对肠道紧密连接蛋白的影响
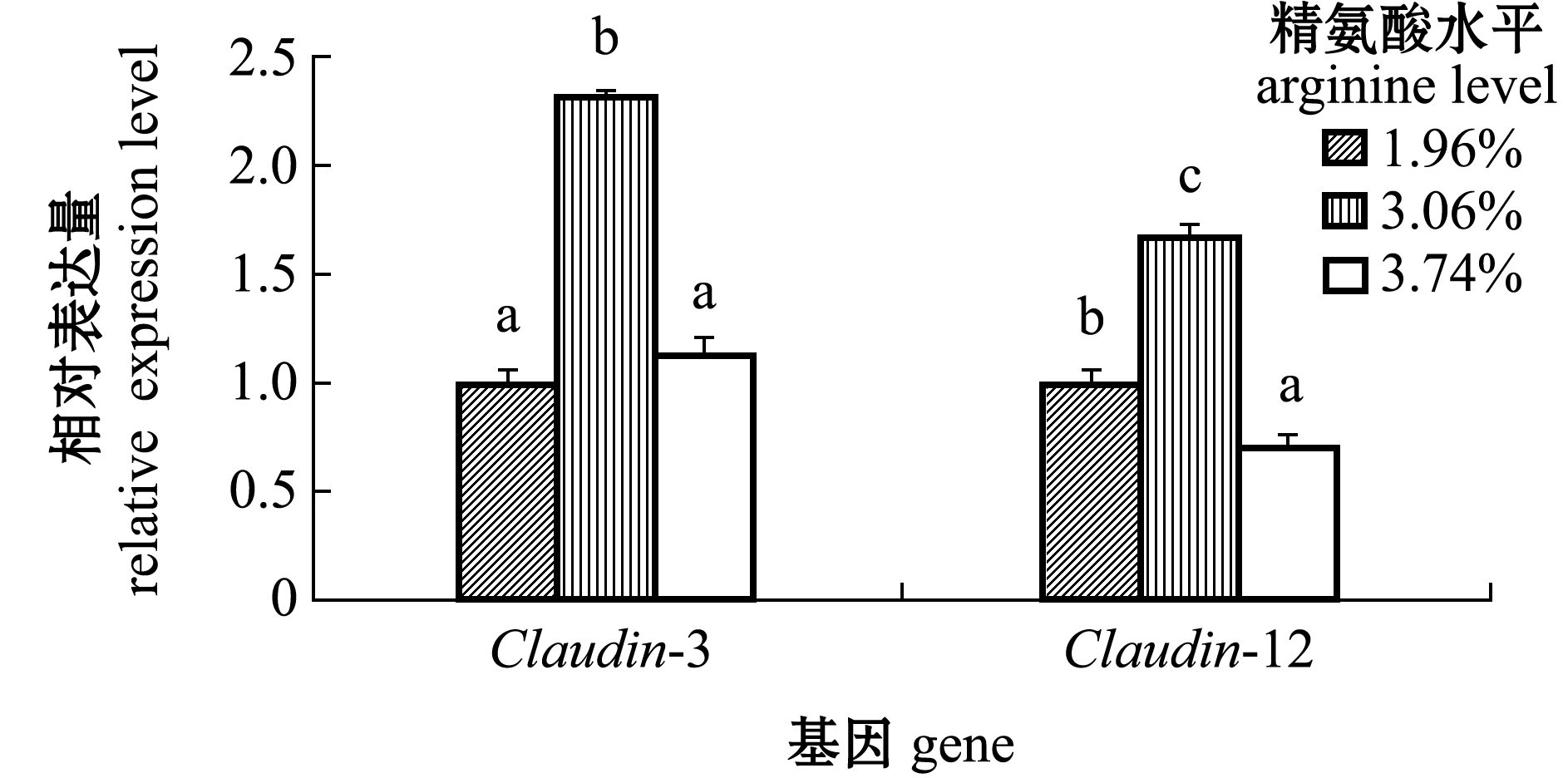
从图7可见:以1.96%精氨酸组为对照,饲粮中含3.06%精氨酸显著上调了珍珠龙胆石斑鱼肠道Claudin-3表达水平(P<0.05),其余两组间相比无显著性差异(P>0.05);1.96%精氨酸组Claudin-12表达量显著低于3.06%精氨酸组(P<0.05),但显著高于3.74%精氨酸组(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
3.1 系统发育树分析
对人类的研究表明,Claudins家族包括25个成员,每一个Claudin分子均由4个跨膜结构域组成,可以与ZO-1、ZO-2及Claudin1-8序列羧基末端结合,还可与邻近细胞相接触,通过同源性或异源性接触调节细胞连接处的选择渗透性[13-14],构成紧密连接复合物的主链。本研究中,通过RT-PCR 技术克隆获得了珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因,Claudin-3 cDNA全长为1 544 bp,其中,开放阅读框为648 bp,可编码215个氨基酸的蛋白,该蛋白含有4个跨膜结构域,而cDNA全长为1 236 bp的Claudin-12基因,可编码341个氨基酸的蛋白,该蛋白含有3个跨膜结构域。通过对各物种氨基酸序列的比对结果进行分析,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-3氨基酸序列与斜带石斑鱼的同源性最高,一致性高达98.14%,与鲈形目关系较远的斑点叉尾鮰(鲇形目)也有70.37%的一致性,整体上氨基酸序列一致性为65.91%~98.14%,由此推测,Claudin-3氨基酸序列具有较高的保守性。通过系统发育树可知,鱼类的Claudin-3 独立聚成一支,最终与其他物种汇聚成的分支聚为一支,虽然位于不同的进化分支,但它们具有一定的亲缘关系。而珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-12与同为鲈形目 科的
科的 有91.79%的一致性,与其他鲀科、花鳉科、鲤科同源性较低,与其余物种氨基酸一致性为50.93%~91.79%。
有91.79%的一致性,与其他鲀科、花鳉科、鲤科同源性较低,与其余物种氨基酸一致性为50.93%~91.79%。
3.2 Claudin-3与Claudin-12在相应组织中的表达机理
Claudin-3蛋白是决定人体血脑屏障紧密连接的主要成分[15]。Clelland等[16]研究显示,Claudin-3蛋白亚型还可能在调节溶质通过上皮细胞旁路的运动中发挥作用,参与鱼类体内盐和水平衡的稳态调控。鱼类的鳃、肾和肠道均为调节机体渗透压的重要器官,本研究中,Claudin-3基因在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼鳃、体肾和中肠中的相对表达量较高,因此,推测珍珠龙胆石斑鱼的Claudin-3基因在鳃、体肾和肠道的结构完整性及其调节水、盐平衡和屏障功能中发挥重要作用。通过抑制小鼠脑毛细血管中Claudin-12基因的表达,可增加脑血管的渗透调节,诱导牛磺酸和肌氨酸等能量缓解物质输入,改变了脑部毛细血管物质转运的功能[17]。本研究中,Claudin-12基因在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼中肠和后肠的表达水平仅低于脑部,高于其他各组织,提示该基因表达水平对肠道的功能具有较大的影响。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼肠道Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因在各组织的整体表达水平表明,其可能在鱼体肠道的水、盐渗透平衡及屏障功能的维护调节方面较多地发挥作用。
3.3 精氨酸对肠道紧密连接蛋白的影响
肠道是鱼类重要的营养和免疫器官之一,发挥消化和吸收营养物质、参与摄食调控类激素的分泌及抵抗病原微生物和食物抗原等作用[18]。紧密连接蛋白在肠道中作为一个高度动态的屏障结构,通过调节细胞间的通透性而选择性吸收水分、离子及营养物质,维持其结构完整性,紧密连接蛋白的表达量在一定程度上可以反映肠道物理屏障功能[19-21],如草鱼中肠损伤后Claudin-12 表达显著降低[22]。营养物质可有助于维持紧密连接蛋白结构完整性,研究表明,精氨酸可通过调节生长中期草鱼紧密连接蛋白基因表达保护铜诱导的破坏鳃上皮屏障结构[23],可以增加草鱼肠道绒毛长度、隐窝深度、肠壁厚度和隐窝宽度,改善营养物质吸收的有效区域,增加营养吸收效率,提高终末体质量[11]。本研究团队前期试验也表明,斜带石斑鱼肠道的皱襞高度和肌层厚度受到精氨酸的显著影响,与其生长状况呈正相关[12]。本试验中,3.06%精氨酸组对石斑鱼生长具有改善作用,而该组肠道Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因mRNA表达也显著上调,生长效果与肠道Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因表达趋势相呼应,进一步说明饲料中适量精氨酸可通过上调石斑鱼肠道Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因表达,改善肠道屏障作用,提高鱼的存活率和增重率。研究表明,不同 Claudins基因异常引起肠道疾病的病理机制不同,如Claudin-3减少溶质和水的细胞旁转运,即增强了屏障作用,而 Claudin-12增加溶质和水的细胞旁转运,即削弱了屏障作用,这分别致使小溶质和水分泌通道增加,可能导致腹泻;大分子的吸收通过通道增加,诱发炎症反应[24]。本试验中,3.06%精氨酸组石斑鱼肠道Claudin-12基因表达上调,结合前期试验切片的观察,不仅未产生石斑鱼肠道炎症,反而改善其生长,同时3.74%精氨酸组该基因表达显著高于1.96%精氨酸组,尽管生长未出现显著性差异,但提示低浓度精氨酸相对于高浓度精氨酸对Claudin-12基因表达有抑制作用。
4 结论
1)使用同源克隆及RACE PCR技术克隆得到珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因的全长,分别为1 544 bp和1 236 bp。
2)Claudin-3基因在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼鳃、体肾和中肠中的相对表达量较高,可能在调节水、盐平衡和屏障功能中发挥重要作用。Claudin-12在中肠和后肠的表达水平仅低于脑部,高于其他各组织,提示该基因表达水平对肠道的功能具有较大影响。
3)饲料中适量精氨酸可通过上调石斑鱼肠道Claudin-3与Claudin-12基因表达,改善肠道屏障作用,从而提高鱼的存活率和增重率。低浓度精氨酸相对于高浓度精氨酸对Claudin-12基因表达有抑制作用。
参考文献:
[1] 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局,全国水产技术推广总站,中国水产学会.2020中国渔业统计年鉴[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2020.
Fishery Administration Bureau of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,National Fisheries Technology Extension Station,China Society of Fisheries.2020 China fisheries statistical yearbook[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,2020.(in Chinese)
[2] 沈桂明.珍珠龙胆石斑鱼幼鱼皮肤溃疡病病原的研究[D].上海:上海海洋大学,2016.
SHEN G M.Studies on the pathogen of skin-ulcer disease in juvenile hybrid groupers Epinephelus fuscoguttatus(♀)×E.lanceolatus(♂)[D].Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University,2016.(in Chinese)
[3] 丛馨,张艳,俞光岩,等.上皮细胞间紧密连接功能的研究进展[J].生理学报,2016,68(4):492-504.
CONG X,ZHANG Y,YU G Y,et al.Research progress on the function of epithelial tight junction[J].Acta Physiologica Sinica,2016,68(4):492-504.(in Chinese)
[4] SUN L Y,LIU S K,BAO L S,et al.Claudin multigene family in channel catfish and their expression profiles in response to bacterial infection and hypoxia as revealed by meta-analysis of RNA-Seq datasets[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D:Genomics and Proteomics,2015,13:60-69.
[5] SYAKURI H,ADAMEK M,BROGDEN G,et al.Intestinal barrier of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.)during a cyprinid herpesvirus 3-infection:molecular identification and regulation of the mRNA expression of claudin encoding genes[J].Fish &Shellfish Immunology,2013,34(1):305-314.
[6] TIPSMARK C K,MADSEN S S.Tricellulin,occludin and claudin-3 expression in salmon intestine and kidney during salinity adaptation[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Molecular &Integrative Physiology,2012,162(4):378-385.
[7] MCLAUGHLIN J,PADFIELD P J,BURT J P H,et al.Ochratoxin A increases permeability through tight junctions by removal of specific claudin isoforms[J].American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology,2004,287(5):C1412-C1417.
[8] 郭晓波.海藻多糖对仔猪小肠上皮细胞屏障功能的调控作用[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2019.
GUO X B.Regulation of seaweed polysaccharide on the barrier function of intestinal porcine epithelial cells[D].Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University,2019.(in Chinese)
[9] ZHANG Y L,DUAN X D,FENG L,et al.Soybean glycinin disrupted intestinal structural integrity related to aggravation of apoptosis and downregulated transcription of tight junction proteins in the intestine of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J].Aquaculture,2021,531:735909.
[10] ZHAO Y,ZHANG T R,LI Q,et al.Effect of dietary L-glutamate levels on growth,digestive and absorptive capability,and intestinal physical barrier function in Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var.Jian)[J].Animal Nutrition,2020,6(2):198-209.
[11] 陈娇娇.精氨酸对草鱼幼鱼生长、肠道结构调控及机制研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2017.
CHEN J J.Studies on the regulation and the related mechanism of arginine on growth and intestinal structure of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2017.(in Chinese)
[12] 迟淑艳,韩凤禄,谭北平,等.饲料精氨酸水平对斜带石斑鱼幼鱼生长和肠道形态的影响[J].水生生物学报,2016,40(2):388-394.
CHI S Y,HAN F L,TAN B P,et al.Effects of dietary arginine level on growth performance and intestine morphology of juvenile grouper Epinephelus coioides[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2016,40(2):388-394.(in Chinese)
[13] ITOH M,FURUSE M,MORITA K,et al.Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs,ZO-1,ZO-2,and ZO-3,with the COOH termini of claudins[J].The Journal of Cell Biology,1999,147(6):1351-1363.
[14] MORIN P J.Claudin proteins in human cancer:promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy[J].Cancer Research,2005,65(21):9603-9606.
[15] WOLBURG H,WOLBURG-BUCHHOLZ K,KRAUS J,et al.Localization of claudin-3 in tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier is selectively lost during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and human glioblastoma multiforme[J].Acta Neuropathologica,2003,105(6):586-592.
[16] CLELLAND E S,BUI P,BAGHERIE-LACHIDANM,et al.Spatial and salinity-induced alterations in claudin-3 isoform mRNA along the gastrointestinal tract of the pufferfish Tetraodon nigroviridis[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Molecular &Integrative Physiology,2010,155(2):154-163.
[17] B LANGER M,ASASHIMA T,OHTSUKI S,et al.Hyperammonemia induces transport of taurine and creatine and suppresses claudin-12 gene expression in brain capillary endothelial cells in vitro[J].Neurochemistry International,2007,50(1):95-101.
LANGER M,ASASHIMA T,OHTSUKI S,et al.Hyperammonemia induces transport of taurine and creatine and suppresses claudin-12 gene expression in brain capillary endothelial cells in vitro[J].Neurochemistry International,2007,50(1):95-101.
[18] DONG B,YI Y H,LIANG LF,et al.High throughput identification of antimicrobial peptides from fish gastrointestinal microbiota[J].Toxins,2017,9(9):266.
[19] 黄妍君.维生素E及其衍生物对肠道屏障结构蛋白的保护作用研究[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2018.
HUANG Y J.The protective effects of vitamin E and its derivatives on tight junction proteins [D].Changsha:Hunan Normal University,2018.(in Chinese)
[20] FANNING A S,MITIC L L,DERSON J M.An barrier transmembrane proteins in the tight junction[J].Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,1999,10(6):1337-1345.
[21] 刘畅.探究TLR4对小鼠肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白的调控作用[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2018.
LIU C.Investigate the regulation of TLR4 on tight junction proteins in mice’intestinal mucosal[D].Shenyang:China Medical University,2018.(in Chinese)
[22] 许凡.草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idellus)肠道紧密连接蛋白基因克隆与表达活性分析[D].苏州:苏州大学,2013.
XU F.Cloning and expression activity analysis of the tight junction protein genes of grass carp,Ctenopharyngodon idellus[D].Suzhou:Soochow University,2013.(in Chinese)
[23] 王标.精氨酸对中期草鱼肉质和铜诱导的鳃屏障功能的影响[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2014.
WANG B.The effect of dietary arginine supplement on flesh quality and Cu-induced gill barrier function of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[D].Yaan:Sichuan Agricultural University,2014.(in Chinese)
[24] TURNER J R,BUSCHMANN M M,ROMERO-CALVO I,et al.The role of molecular remodeling in differential regulation of tight junction permeability[J].Seminars in Cell &Developmental Biology,2014,36:204-212.
 的亲缘关系最近,同源性最高,一致性高达91.75%;Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因在被检测的13种组织中均有表达,Claudin-3 mRNA在鳃和体肾中表达量最高(P<0.05),其次是中肠和肝脏,Claudin-12在脑中表达量最高(P<0.05),其次是中肠和后肠;饲料中精氨酸含量为3.06%时,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼增重率及肠道Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因表达水平显著高于1.96%和3.74%精氨酸组(P<0.05)。研究表明,Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因表达在适宜精氨酸水平的影响下上调,可维护石斑鱼肠道黏膜屏障完整,并促进鱼体生长。
的亲缘关系最近,同源性最高,一致性高达91.75%;Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因在被检测的13种组织中均有表达,Claudin-3 mRNA在鳃和体肾中表达量最高(P<0.05),其次是中肠和肝脏,Claudin-12在脑中表达量最高(P<0.05),其次是中肠和后肠;饲料中精氨酸含量为3.06%时,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼增重率及肠道Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因表达水平显著高于1.96%和3.74%精氨酸组(P<0.05)。研究表明,Claudin-3和Claudin-12基因表达在适宜精氨酸水平的影响下上调,可维护石斑鱼肠道黏膜屏障完整,并促进鱼体生长。









 LANGER M,ASASHIMA T,OHTSUKI S,et al.Hyperammonemia induces transport of taurine and creatine and suppresses claudin-12 gene expression in brain capillary endothelial cells
LANGER M,ASASHIMA T,OHTSUKI S,et al.Hyperammonemia induces transport of taurine and creatine and suppresses claudin-12 gene expression in brain capillary endothelial cells