(1.华中农业大学 水产学院,湖北 武汉 430070;2.华中农业大学 水产养殖国家级实验教学示范中心,湖北 武汉 430070;3.池塘健康养殖湖北省工程实验室,湖北 武汉 430070)
核酸扩增技术,主要指聚合酶链式反应(Polymerase chain reaction,PCR),自1985年首次出现,即被广泛应用于以分子生物学为基础的医学、生物学等领域中,其也是鱼类养殖生产中减少经济损失、防止病害蔓延的一种有效快速检测技术。目前,应用于鱼类病原菌检测的分子诊断技术,如PCR和RT-PCR技术(Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction)等均具有较高的特异性和敏感性。但由于其对高精密的热循环仪器及成像系统的依赖,并存在反应步骤复杂、时间较长等缺点,相关学者一直致力于分子诊断技术的改进和优化。2000年, Notomi等[1]公开了一种适用于核酸检测的环介导等温扩增技术(Loop-mediated isothermal amplification,LAMP),迅速引起了人们的关注,它针对目标DNA链上的6个区段设计4条不同的引物,在Bst DNA聚合酶的催化作用下通过链置换反应在一定温度下快速扩增目的片段。该技术仅利用一个加热设备或者恒温水浴锅维持一定温度即可进行反应,相对于传统PCR和RT-PCR反应来说具有更高的灵敏度和特异性,对于检测结果的观察也更为直观。目前,LAMP已经被广泛应用于人类和动物病原生物的检测,如SARS冠状病毒(SARS-CoV)[2]、H5N1禽流感病毒(H5N1 Avian Influenza viruses)[3]、口蹄疫病毒(Footandmouth disease virus, FMDV)[4]、乙型肝炎病毒(Hepatitis B virus, HBV)[1]等。在水产动物病原的检测方面,LAMP也已得到广泛的应用,如病毒中的虹彩病毒(Iridovirus)[5-6]、疱疹病毒(Herpesvirus)[7-10]等,细菌中的爱德华氏菌属Edwardsiella[11-12]、弧菌属Vibrio[13-15],寄生虫中的黏孢子虫属Myxosporea[16-17]、华支睾吸虫Clonorchis sinensis[18-19]等,并取得了良好的效果。本研究中,对2004年以来国内外学者建立的LAMP法在水产养殖动物常见病原生物快速检测中的应用及对该技术的改进进行简要概述,旨在为该技术在生产一线的应用和推广提供参考。
1 LAMP方法简介
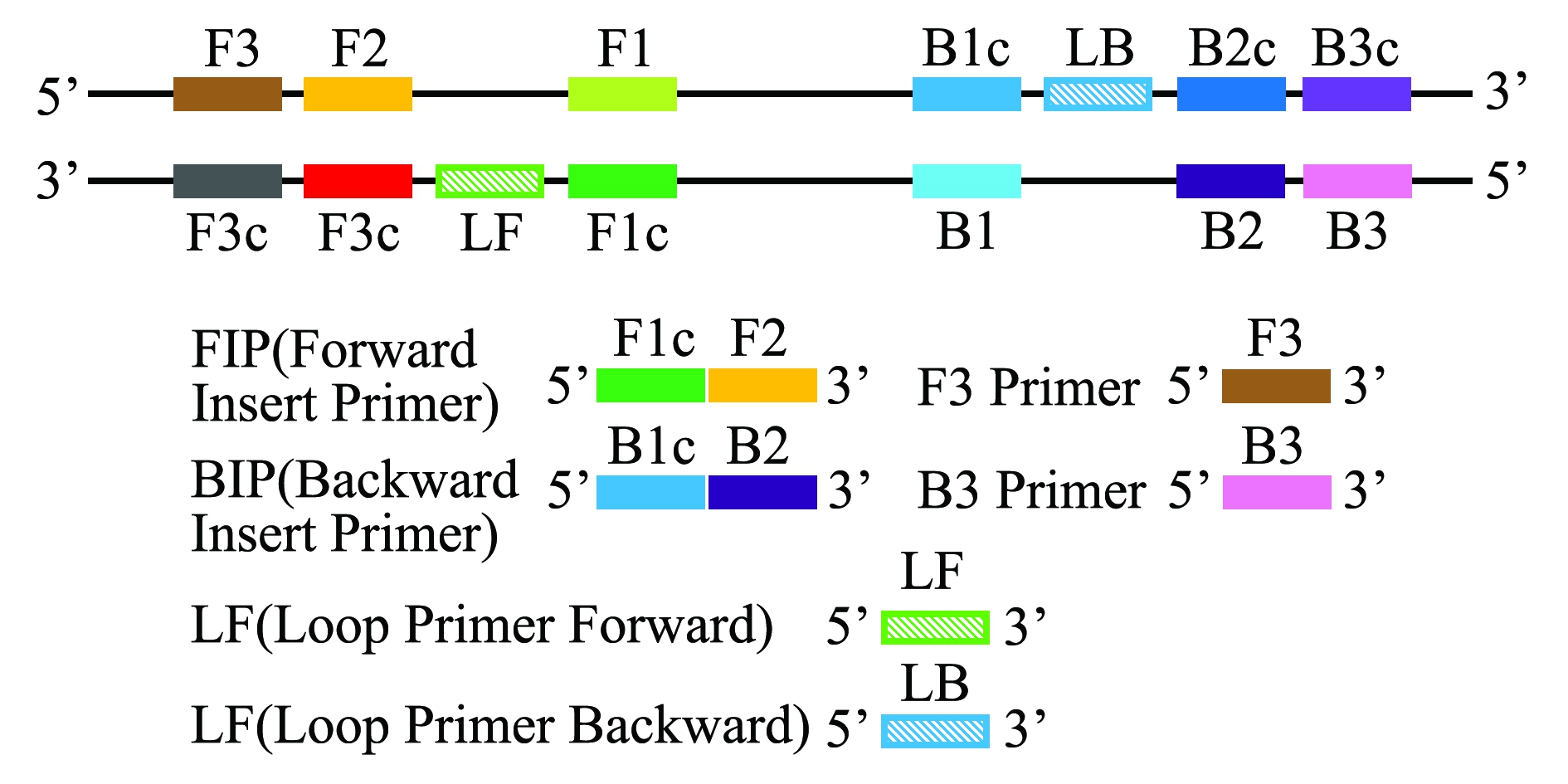
LAMP技术是一种能在等温条件下,利用一组4条特异性引物对极少量的目的DNA片段进行高效、快速和特异性扩增的核酸扩增技术。成环扩增反应能够在1 h内将目的片段的数量累积到109~1010倍。4种引物分别针对特定片段的6个区段(F3、F2、F1、B1、B2和B3)设计,其中正向内引物FIP(Forward insert primer)包括F2和F1c(与F1序列互补)两段序列,反向内引物BIP(Backward insert primer)则包括B2和B1c两段序列(图1)。在起始反应中,4种引物均发挥了作用,在随后的成环反应中则主要是由内引物完成链置换和链合成过程。由于FIP和BIP均包含了目的片段正义链和反义链的两段不同序列,一段序列用于第一阶段的起始反应,另一段序列则用于随后的自动成环反应。LAMP的最大特点是不需要使双链DNA先变性成单链,在等温条件下可持续进行扩增。对于RNA病毒,在反应体系中直接加入反转录酶就可以直接进行快速检测。LAMP扩增的效率和灵敏度也较高,一般在恒定温度下,1 h可以对拷贝的DNA进行109倍扩增[1]。经进一步优化,在反应体系中直接加入环引物LF(Loop Primer Forward)、LB(Loop primer Backward)(这是一种杂交茎环结构),能省略预变性的时间,使得反应时间缩短至0.5 h左右[20-23]。
1.1 引物设计原则
LAMP的引物可在引物设计网站导入靶基因设置相关参数获得。其设计原则与PCR类似,但由于LAMP对引物的要求较高,所以较PCR更为复杂。引物的退火温度(Tm)、引物末端的稳定性、GC含量和引物的二级结构是其引物设计最关键的因素。引物的Tm值通过紧邻分析法估算,一般要求F1c和B1c的Tm值为64~66 ℃;F2、F3、B2、B3的Tm值为59~61 ℃,即二者温差为5 ℃较好,环引物的Tm值同F1c和B1c。引物末端的稳定性由自由能改变值(△G)来衡量,一般要求F2、B2、F3、B3的3′端和F1c、B1c的5′端的△G小于或等于-4 Kcal/mol。此外,当引物的GC含量为50%~ 60%时,质量较高,根据实际情况将条件适当放宽至40%~65%也可。另外,设计的引物自身或引物间要求不能形成二级结构。对于引物间的距离也有要求,F2末端和B2末端的区域应介于120~160 bp,F2的5′端和F1的5′端间成环区域的间距为40~60 bp,F2到F3间的距离为0~60 bp(B2同B3)。此外,由于链的取代反应是限速步骤之一,因此,要求目的片段小于300 bp。
1.2 反应条件
一般来说,LAMP方法的建立涉及到引物及其浓度、反应温度、反应时间、Mg2+最适浓度等反应条件的优化。引物的最适比例需要通过具体试验确定,一般内引物、外引物、环引物的比例以8∶1∶4较为适合[21],Zhang等[22]在蛙病毒属Ranavirus的LAMP中发现,三者的最佳比例为10∶1∶5;Suebsing等[23]使用10∶1∶10的比例检测大马哈鱼Oncorhynchus keta传染性造血器官坏死病毒(Infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus,IHNV)也收到了较好的效果。一般来说,其他两对引物比例不变的条件下,适当增加内引物的浓度,可以提高反应的灵敏度,而外引物的浓度增加则对灵敏度无明显的影响[24]。
反应条件中Mg2+的浓度也是非常关键的一个因素,在众多已建立的LAMP检测方法中,Mg2+较为常见的终浓度为6 mmol/L,效果最好[23],也有报道认为,体系中Mg2+的终浓度为8 mmol/L[25]和10 mmol/L[26]时产物的条带更为清晰。
此外,也有学者研究在内引物F1c(B1c)与F2(B2)之间分别插入2、4、6个T作为连接子,比较其对反应结果的影响[27],结果表明,插入4个T和6个T均能完成反应,其中,4个T的插入使得目的产物的条带比不插入任何碱基时更清晰,Jeon等[17]的研究也证实了这一点,而2个T的插入可能抑制成环过程,导致反应不能正常进行。
1.3 产物的检测
作为一种核苷酸的扩增反应,LAMP无疑可采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行分析,可以通过是否在理论位置产生有梯度的条带来判断靶基因是否存在,另外,有无杂带和引物二聚体还可作为引物的评判标准。此外,LAMP还有许多更为直观简便的方法来检测产物。
在LAMP反应过程中,焦磷酸离子从dNTPs中释放后与Mg2+结合形成焦磷酸镁沉淀(Mg2P2O7),此衍生物与生成的反应扩增产物成正比,与病原的DNA拷贝数也具有显著的相关性[28],随着反应产生大量的扩增产物,衍生物的产量也会增加,直至出现白色浑浊,可通过肉眼观察反应管中白色沉淀的有无来判断病原是否存在,免去了琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,也有研究使用浊度仪来检测反应管的浊度。
单凭肉眼或分光光度计来分辨浊度变化并不直观,轻度的阳性反应有可能会被误认为是阴性。因此,关于结果判断,学者们希望找到更为直观有效的方法。例如,在LAMP反应结束后加入DNA插入染料,如SYBR green、picogreen或 propidium iodide。其中SYBR green使用较为广泛,该染料能与所有dsDNA双螺旋的小沟区域结合,结合后原来游离状态下的微弱荧光瞬间增强,可以指示反应体系中的扩增产物形成与否。近年来,用FITC(Fluorescein isothiocyanate)标记杂交探针与生物素标记的扩增产物进行特异性杂交,通过横向流动试纸(Lateral flow dipstick,LFD)判读结果的环介导等温扩增联合横向侧流试纸法(LFD-LAMP)也得到越来越多的应用。即以扩增的目标片段中的一段序列作为模板,设计异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)探针,或用FITC标记环引物(LP或者LB)的其中一条作为探针,利用试纸检测线上抗FITC抗体是否与FITC标记的扩增产物结合引起显色反应来指示目标片段存在与否和是否发生扩增[24],并用生物素标记内引物的5′端,作为质控的显色标记。如嗜水气单细胞菌Aeromonas hydrophila的快速检测[29]和传染性脾肾坏死病毒(Infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus,ISKNV)的检测[30]等,后者全程仅需25 min,最低检测浓度为10个拷贝/反应,其灵敏度和反应速度均优于常规的PCR反应。
以上方法均需要在反应结束后开盖检测,因此,都有被污染的风险。2013年,Suebsing等[31]在建立的海豚链球菌Streptococcus iniae和无乳链球菌S.agalactiae的LAMP检测中,在反应前预先加入终浓度为25 μmol/L的钙黄绿素染液,实现了不开盖显色检测,避免了开盖后的气溶胶污染。反应前,染液中的Mn2+与钙黄绿素结合处于淬灭状态呈橘黄色,一旦LAMP反应触发后,锰离子与扩增产物的副产物焦磷酸镁发生置换,焦磷酸离子与锰离子结合形成难溶的焦磷酸锰沉淀,钙黄绿素得到释放,淬灭状态解除,发出黄绿色荧光。可以通过肉眼进行比较,判断出扩增结果,在较大程度上避免了开盖造成的假阳性污染。
1.4 避免假阳性的方法
由于LAMP技术1 h就能对拷贝的DNA进行109倍扩增,从而使操作过程中稍有不当即易产生气溶胶污染,最终导致假阳性结果的出现,影响实际生产与应用。避免假阳性的方法有两种:一是闭管检测,防止产物形成气溶胶;二是降解气溶胶上的产物。对于第一种方法应用较为广泛的是检测产物浑浊度或通过钙绿黄素染液显色实现不开盖检测。第二种方法主要是在反应体系中引入dUTP进行预扩增,并加入有效的尿嘧啶核苷酸(UNG)降解含有dUTP的扩增产物,能有效防止遗留物的污染[32],此说法在不少文献中得到了验证[33-34]。
2 LAMP技术在水产病害中的应用
2.1 LAMP技术在病毒检测中的应用
2.1.1 对虾白斑综合症病毒的检测 对虾白斑综合征病毒(White spot syndrome virus,WSSV)是一种具有囊膜、无包涵体的杆状DNA病毒,毒力极强。1992年的研究发现,此病毒主要引起虾的头胸甲、皮下和附肢出现白色斑点,1993年研究发现,此病毒引起的对虾暴发性流行病给亚洲对虾养殖产业造成了巨大冲击[35]。由于缺乏特异性免疫应答机制,因此,通过早期诊断技术筛选健康亲虾,切断病原垂直传播或培育抗病原的新品种对于虾病防治尤为重要。2004年,Kono 等[36]基于WSSV全DNA序列创建了在65 ℃、60 min条件下快速检测对虾白斑综合征病毒的LAMP方法,给该病毒的早期快速诊断带来了福音。2011年,冯华等[37]对于该方法的研究表明,LAMP检测的敏感性显著高于巢式PCR。随后,Chou等[38]将LAMP技术与荧光共振能量转移技术(Fluorescent resonance energy transfer,FRET)结合对WSSV的LAMP检测方法进行了优化,有效提高了检测的特异性。何琳[34]在后期的研究中不仅对反应条件重新进行了优化,建立了WSSV和传染性皮下和造血组织坏死病毒(Infection hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus,IHHNV)多重检测技术,同时先后在反应体系中引入dUTP 和UNG酶来消除LAMP技术的假阳性现象,也能有效地避免反应过程中的污染。
2.1.2 水生呼肠孤病毒的检测 水生呼肠孤病毒(Aquareovirus,ARV)是一类感染水生生物的呼肠孤病毒,主要通过呼吸器官和肠道感染宿主,能引起肝胰脏疾病及出血病症,给水产养殖业带来了不可估量的损失[39]。草鱼呼肠孤病毒(Grass carp reovirus,GCRV)是中国分离鉴定的第一株鱼类病毒,同时也是对草鱼Ctenopharyngodon idellus危害非常大的一株病毒,可能会引起草鱼出血病的暴发。Zhang等[40]通过往反应体系中直接加入反转录酶建立了GCRV的RT-LAMP(Reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification)检测方法,并对Mg2+浓度、反应温度、时间等反应条件进行了优化,结果比传统RT-PCR灵敏度更高。2013年,Zeng等[41]又基于GCRV的s6基因设计了包括两条环引物的6条RT-LAMP引物,环引物的加入进一步缩短了检测过程,40 min即可完全反应,检测的最低浓度为10个拷贝/μL,比RT-PCR高出10个数量级,且准确性也比RT-PCR要高。2011年,Chen等[42]建立了泥蟹锯缘青蟹呼肠孤病毒(Scylla serrata reovrirus,SSRV)的LAMP快速检测方法,该方法在62 ℃、60 min条件下灵敏度可达0.8 fg/反应,比传统的RT-PCR高出1000倍。2016年,Ma等[43]又对中华绒螯蟹呼肠孤病毒(Eriocheir sinensis reovirus,ESRV)建立了LAMP检测法,在65 ℃恒温条件下仅需45 min即可检测出病原,灵敏度为15 fg/反应,也比传统RT-PCR反应高出了100倍。
2.1.3 虹彩病毒的检测 虹彩病毒(Iridovirus)是一种胞浆型DNA病毒,主要引起鱼类和蛙类等动物的疾病。对该病毒的LAMP研究最早出现在2004年,Caipang等[28]针对真鲷科鱼类中的虹彩病毒(RSIV)建立的LAMP检测法,发现其灵敏度比常规PCR反应高10倍。2008年,Mao等[6]应用LAMP技术对新加坡石斑鱼虹彩病毒(Singapore grouper iridovirus,SGIV)进行快速检测,结果表明,在65 ℃、20 min水浴条件下最低检测限度为0.02 fg(6.3拷贝数)/反应。2009年,Zhang等[5]基于Msp I限制性DNA片段对新发现的病毒——大菱鲆红体病虹彩病毒(Turbot reddish body iridovirus,TRBIV)建立了快速检测方法,该方法灵敏度是常规PCR反应的100倍。2016年,Suebsing等[44]基于一种主要的衣壳蛋白基因建立了罗非鱼Oreochromis spp.传染性脾肾坏死病毒(ISKNV)的羟基萘酚蓝-LAMP法,研究ISKNV在罗非鱼体内的转移。该方法的最佳反应条件为65 ℃、45 min,其能通过颜色的变化特异性检测到病原菌,在ISKNV感染的罗非鱼池塘中病原检出率比普通PCR反应高出41.33%。红色罗非鱼O.niloticus×O.mossambicus的原位LAMP试验结果显示,ISKNV存在于生殖腺中,阳性信号仅存在于卵泡中,卵母细胞中并没有,而组织趋向性试验结果表明,脑是ISKNV在红色罗非鱼(40%)和尼罗罗非鱼O.niloticus(20%)中感染的主要靶器官。
虹彩病毒中的大鲵蛙病毒(Ranavirus)是一种新型病原微生物,表现为大鲵Andrias davidianus体表出现溃烂并出现血红色斑点。2013年,Zhang等[22]建立了蛙病毒属的LAMP检测方法,能够成功检测出大鲵虹彩病毒(Andrias davidianus iridovirus,ADIV)、中华鳖虹彩病毒(Soft-shelled turtle iridovirus,STIV)和流行性造血器官坏死病毒(Epizootic hematopoietic necrosis virus,EHNV),且对锦鲤疱疹病毒(Koi herpes virus,KHV)、斑点叉尾鮰病毒(Channel catfish virus,CCV)、传染性肝肾坏死病毒(ISKNV)和白斑综合征病毒(WSSV)等无交叉反应,最低检测浓度为100个拷贝数/μL的STIV病毒DNA片段,灵敏度比普通PCR反应高10倍。2014年,刘星星等[45]建立和优化了大鲵蛙病毒LAMP方法,在62 ℃、40 min水浴条件下即可完成反应,且优化反应体系后的LAMP比巢式PCR最低检出率高1个数量级,比普通PCR高3个数量级,特异性强且与多种病毒均无交叉反应。
2.1.4 弹状病毒的检测 弹状病毒科Rhabdoviridae的病毒粒子形态似棒状或子弹状,病毒在细胞质内增殖,鲤春病毒血症病毒(Spring viraemia of carp virus,SVCV)、病毒性出血性败血症病毒(Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus,VHSV)、传染性造血器官坏死病毒(Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus,IHNV)均属于此类病毒。
Gunimaladevi等[46]在2005年基于G蛋白基因同时建立了虹鳟Oncorhynchus mykiss传染性造血坏死病毒的RT-LAMP和LAMP检测方法。结果表明,在63 ℃、60 min 条件下RT-LAMP与LAMP的结果类似,灵敏度均比传统巢式PCR高出10倍。2011年,Suebsing等[23]基于同一个基因建立了大马哈鱼该病毒的快速检测方法,由于环引物的作用,该方法30 min内即可检测到IHNV的扩增产物。检测限度为0.01 fg/μL,同样比巢式RT-PCR高出10倍,且在473份样品中,RT-LAMP的阳性检出率为40.38%,而RT-PCR的检出率为34.25%。病毒性出血性败血症病毒的RT-LAMP检测方法则于2006年被Soliman等[21]建立,环引物的加入使得反应时间由60 min缩短至30 min,值得一提的是,该反应的灵敏度与常规PCR反应一致。
2008年,Shivappa等[47]基于糖蛋白G的核苷酸序列建立了鲤春病毒的RT-LAMP法,连续稀释SVCV 样品的结果与RT-PCR相似,最低稀释至10 TCID50/mL,同样可以被检测出。同年,Mao等[6]基于M基因建立了该病毒的一步式RT-LAMP检测方法,灵敏度比RT-PCR反应高10倍,对472尾样品鱼的检测结果表明,该方法与标准病毒分离方法的检测结果一致。
2.1.5 疱疹病毒科的检测 疱疹病毒(Herpes simplex virus,HSV)的检测方法有许多,如活细胞分离、电镜扫描、PCR检测、ELISA和原位杂交等,但均耗时耗力,且对设备的要求非常高。2004年,Gunimaladevi等[7]基于胸苷激酶基因(tk)序列建立了鲤Cyprinus carpio L.锦鲤疱疹病毒(KHV)的LAMP检测方法,最适反应条件为65 ℃、60 min,灵敏度与普通PCR一致,能从患病鱼的鳃、肝和肾脏组织中检测到病毒,而普通PCR则仅能从鳃组织中检测到病毒。2005年,Soliman等[48]比较了该病毒感染后的组织经不同的处理方法对检测结果的影响,发现该方法对沸煮法提取的DNA同样适用。2009年,Yoshino等[8]也对该病毒的LAMP检测方法开展了相关研究。
随着时间的推移,鲤科疱疹病毒2型(Cyprinid herpesvirus 2,CyHV-2)和3型(Cyprinid herpesvirus-3,CyHV-3)的LAMP检测法也相继被建立。2013年,He等[9]基于末端酶基因建立了金鱼CyHV-2的LAMP检测法,该方法检测的最低核酸浓度为1.09×10-4 μg/μL,高于常规PCR和实时荧光定量PCR试验。异育银鲫Carassius auratus gibelio中该病毒的LAMP检测法于2014年分别由中国水产科学研究院长江水产研究所Zhang等[49]、Liang等[10]基于DNA解旋酶基因和ITP基因建立,后者能检测到10个拷贝/μL的病原,比PCR反应高出2个数量级,经过对120个异育银鲫样品检测结果表明,阳性检出率为92.5%,高于普通PCR试验(70.8%)。2015年,Zhu 等[50]建立了异育银鲫出血病病原(疑似CyHV-2)的LAMP检测法,该方法能从流行地区无明显症状的鱼体内和患病鱼卵中检测到病原的阳性信号,提示该病原具有潜伏期且可能具有垂直传播能力。总之,对于CyHV-2的LAMP检测方法已非常成熟,可应用于批量检测和早期诊断。
2009年,Soliman等[51]分别引入免疫捕捉(Immuno capture,IC)和直接结合(Direct bonding,DB)技术建立了CyHV-3的IC-LAMP和DB-LAMP检测法,两种方法均能成功检测到病原的阳性信号,DB-LAMP的最低检测浓度为0.1 virus particles/mL,比IC-LAMP高10倍。相比较于常规PCR反应的5 h来说,DB-LAMP反应在90 min内即可完成。DB-LAMP简便、快速且敏感,可应用于CyHV-3的野外诊断。2010年,Soliman等[52]基于TK基因建立了CyHV-3的RT-LAMP联合核酸横向侧流法,该方法的最低检测限度为10 fg DNA目的片段/反应,相当于30个基因组拷贝。其灵敏度与LAMP反应相当,但能在5 min内显示结果,进一步节省了时间。
疱疹病毒科的淋巴肿瘤病毒(Lymphocystis disease virus,LCDV)的LAMP检测法也同样被建立。2010年,Li等[53]基于主要的衣壳蛋白基因建立了LCDV的LAMP检测法,最低检测浓度为15 fg/反应,与实时荧光定量PCR的最低检测浓度接近,但比常规PCR高10倍,经过对109份临床样品检测表明,该方法是一种快速便捷的LCDV野外诊断工具。2017年,Valverde等[54]基于MCP基因建立了LCDV-VII型的RT-LAMP检测法,该方法能检测到无病症的病毒携带鱼,最低检测浓度为10个病毒DNA拷贝/反应。
2.1.6 Beta诺达病毒(神经坏死病毒)的检测 罗氏沼虾Macrobrachium rosenbergii的白尾病是由诺达病毒(Macrobrachium rosenbergii noda virus,MrNV)和额外的小病毒(Extra small virus,XSV)共同造成的一种疾病,这种病的RT-LAMP快速检测法在2006年被Pillai等[55]建立。该方法设计了内、外引物各一对用来检测MrNV,由于XSV通常更易降解且感染剂量较小,因此,另外设计一对环引物用于加速对XSV的检测。未加环引物的RT-LAMP法对MrNV的检测灵敏度比RT-PCR高10倍,对XSV的检测灵敏度没有显著差异。而加入环引物的RT-LAMP反应则能使XSV的检测灵敏度提高至少10 000倍。
神经坏死病毒(Nervous necrosis virus,NNV)的鱼类宿主较为广泛,对该病毒的RT-LAMP检测方法的研究也比较热门,2009年至今,学者们先后从石斑鱼Epinephelus sp.、牙鲆Paralichthys olivaceus、七带石斑鱼E.septemfasciatus等鱼类[27,56-58]中分离到该病毒,基于该病毒的衣壳蛋白编码基因、RdRP基因建立了RT-LAMP检测法。其中,Suebsing等[57]的方法灵敏度最高,分别比巢式RT-PCR和RT-PCR高100倍和10 000倍。该方法能特异性地检测条纹鲹神经坏死病毒(Striped jack nervous necrosis virus,SJNNV)和赤点神经坏死病毒(Red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus,RGNNV),其他病毒样品均显示阴性结果。2009—2011年对102尾牙鲆的检测数据表明,RT-LAMP的NNV检出率(53.9%)同样高于巢式RT-PCR(33.8%)。Sung等[56]、Mekata等[58]、Hwang等[27]建立的RT-LAMP检测法灵敏度略低,但仍高于或与巢式RT-PCR相当,但比起常规RT-PCR来说优势非常明显,且在时间和试剂的消耗上更胜一筹。
2010年,Xu等[59]基于基因组RNA建立了卵形鲳鲹Trachinotus ovatus RGNNV的LAMP法,灵敏度比巢氏PCR反应高100倍,能从出现典型病症的患病卵形鲳鲹脑中检测到病原信号。
2.1.7 双RNA病毒的检测 传染性胰腺坏死病毒(Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus,IPNV)是鲑鳟鱼类的主要传染病原之一[60],大西洋鲑Salmo salar和大马哈鱼IPNV的检测方法分别由相关学者于2009年[61]和2011年[62]建立,两种方法的反应条件均为65 ℃,前者能从IPNV感染的大西洋鲑肾组织中检测到该病毒,最低检测浓度为0.001 fg RNA/反应,最适反应条件为60 min。后者在30 min内对IPNV感染的虹鳟性腺2期细胞的最低检测浓度为0.075 TCID50/mL,比巢式RT-PCR反应高出100倍,对659份野外样品检测表明,RT-LAMP的检出率(40.4%)也高于巢式RT-PCR(27.6%)。此外,建立大马哈鱼IPNV快速检测法的Suebsing等[63]同年分别构建了虹鳟IPNV、造血性坏疽病毒(Hematopoietic necrosis virus,IHNV)和出血性败血症病毒(Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus,VHSV)3种病毒病的RT-LAMP检测法。在2年的观测期内,抽检样品中有53.5%的虹鳟经检测为IPNV阳性,其他两种病毒未被检出。
2009年,Andrade等[64]基于衣壳蛋白基因建立了传染性肌肉坏死病毒(Infectious myonecrosis virus,IMNV)的RT-LAMP联合核酸横向侧流法(Reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification and nucleic acid lateral flow,RT-LAMP-NALF),该方法灵敏度比RT-PCR和RT-LAMP法分别高出100倍和10倍,比巢式RT-PCR和实时RT-PCR分别降低了90%和99%。
2.1.8 其他病毒科的检测 其他病毒科的检测主要针对传染性皮下及造血组织坏死病毒(IHHNV)和Fathead minnow nidovirus(FHMNV)两种。2006年,Sun等[65]建立了IHHNV的LAMP检测方法,可通过凝胶电泳检测到5~500拷贝的片段,比普通PCR灵敏度高出100倍。刘淼等[60]在2010年根据该病毒保守性区域的非结构蛋白基因NS1设计引物,将灵敏度提高到100个拷贝/μL,高于普通PCR 1000倍。2011年,Arunrut等[66]又将横向流试纸与LAMP技术结合到一起,从而明显缩短了检测时间,使得试验时间仅需50 min。2014年,Zhang等[25]基于纤突蛋白基因建立了FHMNV的RT-LAMP检测法,在63 ℃、40 min水浴条件下即可完成反应,最低检测限度为5个病毒拷贝/反应,灵敏度比常规RT-PCR高出1000倍,样品检测结果表明,当鱼组织中病原拷贝数达到4.7×1010 个/mg时,即能被该方法检测到。
2.2 LAMP技术在细菌检测中的应用
2.2.1 弧菌属的检测 弧菌的菌体短小,弯曲成弧形,是一种革兰氏阴性菌,同时也是引起鱼类细菌性疾病的重要病原菌之一。其流行面积广,发病率高,给养殖业造成了极大危害,LAMP方法在弧菌的检测上应用最为广泛。
2009年和2010年,学者分别基于Ompk基因[67]和gyrB基因[13]建立了溶藻弧菌V.alginolyticus的LAMP检测法,后者的最低检测浓度为3.7 CFU/反应。2015年,Plaon等[68]基于rpoX基因设计目的片段,建立了该菌的LFD-LAMP检测方法,在5 min内即可完成检测,进一步避免了假阳性污染并缩短了检测时间。
Yamazaki等[69]在2008年第一次将LAMP方法应用于副溶血弧菌V.parahemolyticus的检测中,对养殖对虾样品进行检测后发现,LAMP对组织中副溶血弧菌的最低检测限度为2.0 CFU/反应,高出PCR的10倍。2014年,Zeng等[70]又将免疫磁化分离(Immunomagnetic separation,IMS)技术与LAMP技术相结合,利用磁性纳米粒子携带的单克隆抗体捕获靶细胞,进行非特异性结合使得检测灵敏度大大提高。
LAMP技术在创伤弧菌快速检测中的应用始于2008年,Han等[71]研究发现,在该菌感染的牡蛎Ostrea gigas组织匀浆中检测到的最低浓度约为107 CFU/g,经过5 h的浓缩后可将浓度降低至7 CFU/g,这种检测方法是PCRs灵敏度的1000倍。在此基础上,2010年Han等[72]将普通LAMP改进为了实时定量检测,通过荧光与浑浊度的方法同时进行结果判读。为了提高检测效率,2016年,Wang等[73]分别基于toxR基因与rpoS基因建立了双重核酸限制性内切酶实时LAMP技术(Multiple endonuclease restriction real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology,MERT-LAMP)对副溶血弧菌和创伤弧菌V.vulnificus同时进行快速检测。同年,Zhou等[74]分别基于鱼肠道弧菌V.ichthyoenteri的ToxR基因、副溶血弧菌的OmpA基因、大菱鲆弧菌V.scophthalmi的luxR基因、创伤弧菌的金属蛋白酶基因,设计了4组内引物含有不同限制性位点的特异性引物,建立了4种弧菌的四重LAMP检测法,灵敏度比常规PCR方法高出100~1000倍。
除上述较常见的弧菌外,贝类动物哈维氏弧菌V.harveyi的LAMP检测方法由Cao等[75]在2010年建立,大菱鲆弧菌V.scophthalmi的LAMP快速检测方法由高志鑫等[76]在2015年建立,特异性均较强,与其他弧菌均无交叉反应。后者更是在30 min内即可完成反应。
2.2.2 链球菌属的检测 链球菌Streptococcus是一种革兰氏阳性球菌,对水产养殖业的危害极大,链球菌病主要是由无乳链球菌S.agalactiae和海豚链球菌S.iniae[77]引起。在养殖罗非鱼中对于海豚链球菌的LAMP检测技术最早由Han等[72]于2011年基于pgm基因建立,随后Cai等[78]和郑磊等[79]均开展了罗非鱼中该菌的LAMP研究,后者选择cfb基因作为目的基因,灵敏度高达30 CUF/mL,是快速诊断罗非鱼无乳链球菌的有效途径。2013年,Suebsing等[31]预先加入钙黄绿素建立了海豚链球菌和无乳链球菌的不开盖快速比色LAMP法,王瑞娜等[80]也在该菌的LAMP检测法中增加了横向流动试纸条技术,这些优化均能较好地避免开盖对试验结果造成假阳性污染。红尾皇冠鱼Aequidens rivulatus无乳链球菌的LAMP检测方法则由姚学良等[81]在2014年基于cfb基因建立,同样具有较高的特异性和稳定性。
2.2.3 气单胞菌属的检测 气单胞菌Aeromonas是一种需氧或兼性厌氧的革兰氏阴性短杆菌,两端钝圆,具单极鞭毛,通常嗜水气单胞菌A.hydrophilia在水产病害中较为常见。程天印等[82]在2007年基于嗜水气单胞菌气溶素基因aerolysin的序列设计引物建立了相应的LAMP检测法,该反应在63 ℃水浴条件下需要90 min完成扩增。同年,匡燕云[83]建立的该菌的LAMP检测法,其目的基因的最低检测限度为38 fg/反应,比普通PCR反应高1000倍,且通过设计并加入环引物,将反应时间缩短至30 min。为了避免开盖检测造成的假阳性污染,蔡怡等[29]又将环介导等温扩增联合横向测流试纸(LAMP-LFD)应用于嗜水气单胞菌的检测中,使LAMP扩增到LFD结果判读只需要40 min。2014年,李嘉彬等[84]又分别建立了嗜水气单胞菌和温和气单胞菌A.sobria的快速检测方法,最低检测限度依次为46、320 fg/mL,是普通PCR方法的10000倍和100倍。此外, 2013年,王子浩[33]建立了维氏气单胞菌A.veronii的LAMP方法,在63 ℃、40 min水浴条件下即可完成反应,模板的最小检测浓度为1.8 fg/μL,人工攻毒后4 h用LAMP检测法即能在患病鱼组织中检测到病原菌,而PCR则需6 h才能检测到。同时该方法也提出可通过分区操作、轻微操作和使用尿苷酸等方法来避免气溶胶的污染。
2.2.4 爱德华氏菌的检测 爱德华氏菌属Edwaradsiella是最早运用LAMP方法进行检测的一类鱼类病原生物。2004年, Savan等[11]首次将这一方法应用到鱼类迟缓爱德华氏菌E.tarda的检测中来,该方法在65 ℃、45 min水浴条件下即可扩增出相应产物,最低可检测出6个DNA拷贝/反应。2013年,Xie等[26]又基于hlyb基因的上游序列建立了该菌的LAMP检测法,能检测的最低浓度为10 CFU/反应,且与同属其他爱德华氏菌不存在交叉反应。
2005年,Yeh等[12]基于eipl8基因建立了斑点叉尾鮰Ictalurus punctatus爱德华氏菌属的LAMP检测方法,检测的最低浓度为20 CFU/反应,能从患病鱼的脑组织检测到病原菌。
2.2.5 其他病原菌的检测 除了上述列出的病原菌,目前已建立LAMP检测方法的还有诺卡氏菌Nocardia seriolae[85]、柱状黄杆菌Flavobacterium columnare[86]、噬冷黄杆菌F.psychrophilum[87]、鲑肾杆菌Renibacterium salmoninarum[88-89]、鲁氏耶尔森氏菌Yersinia ruckeri[90]、弗朗西斯菌Francisella piscicida[91]、恶臭假单胞菌Pseudomonas putida[92]和鱼类格氏乳球菌Lactococcus garvieae[93]等。其中,Fujiwara-Nagata等[87]在噬冷黄杆菌的LAMP检测中发现,反应完成时间与病原菌拷贝数具有明显的相关性。Gahlawat等[89]用LAMP同样能检测到qPCR显示阳性的感染S.salmoninarum的虹鳟巨噬细胞和肾脏组织中的病原菌,灵敏度比qPCR高出一个数量级。Mao等[92]建立的P.putida LAMP检测法以rpoN基因为目的基因,其最低检测限度为4.8 CFU/反应,能从其他9种革兰氏阴性菌中特异性地鉴别出所有P.putida,也能从患病鱼组织中检测到病原菌的DNA片段。Tsai等[93]用LAMP检测L.garvieae时发现,人工感染的罗非鱼和鲻鱼Mugil cephalus的脾、肾和脑组织中均能检测到病原菌,此外,同时用细菌裂解物和纯培养菌株的DNA作为模板,前者更能体现出LAMP相比较于PCR在灵敏度上的优越性。
2.3 LAMP技术在寄生虫检测中的应用
寄生虫也是危害生物安全的病原体之一,一般来说,PCR在DNA检测寄生虫中应用比较普遍。近年来,随着LAMP技术的日趋成熟,脑黏体虫Myxobolus cerebralis、黏孢子虫Kudoa septempunctata、日本血吸尾蚴Schistosoma japonicum Katsurada、贝类派琴虫Perkinsus spp.和包纳米虫Bonamia spp.、华支睾吸虫等寄生虫的LAMP检测方法也相继建立起来。
2005年,El-Matbouli等[94]基于18S rDNA基因建立了鱼和寡毛类脑黏体虫的LAMP检测法,寄生虫的DNA片段可在寡毛类、臀鳍、尾鳍、背鳍和鳃盖的黏液中检测到,该方法能检测的最低限值与PCR反应接近,但更为快速和简便。2005年,El-Matbouli等[16]基于SSU rDNA基因建立了能引起鲑鳟鱼肾肿大病的黏孢子虫新种K.bryosalmonae的LAMP检测法,灵敏度比常规PCR反应高100倍。2014年,Jeon等[17]基于28S rDNA基因建立了褐牙鲆Paralichthys olivaceus黏孢子虫的LAMP检测法,反应条件为63 ℃、45 min,灵敏度比常规PCR反应高10倍。2015年,又一种寄生于褐牙鲆体内黏孢子虫的LAMP检测法和色谱分析法(Nucleic acid sequence based amplification-nucleic acid chromatography,NASBA-NAC)被Sugita-Konishi等[95]建立,结果表明,色谱分析法的灵敏度与定性PCR反应相当,而实时荧光LAMP则与实时荧光定量PCR相当。由于这两种方法能在45 min内发生反应,因此,比其他检测方法在时耗上更具优势。
尾蚴是日本血吸虫的感染期,主要寄生在螺体内,对水生动物和人类危害极大。2008年杨秋林等[96]利用尾蚴钙结合蛋白基因建立了一种可以快速且特异性检测出日本血吸尾蚴的LAMP法。随后,邓鹏程[97]在此基础上又建立了日本血吸虫感染性钉螺、卡氏肺孢子虫Pneumocystis carinii、恶性疟原虫Plasmodium falciparum的环介导等温扩增,敏感度分别是1 pg DNA/μL、1 pg DNA/μL和1.5个疟原虫/107 RBC。
LAMP技术应用于鱼类华支睾吸虫的检测始于2010年,由Cai等[18]建立的该方法在63 ℃、40 min水浴条件下即可完成扩增,在患病鱼的肾和脾脏组织中均能检测到病原,灵敏度为10-2 fg/μL,比传统的PCR反应高出100倍。2013年,Chen等[19]建立了寄生于淡水螺类的华支睾吸虫的LAMP检测法,该方法最低检测浓度为10 fg/反应,比常规PCR反应高1000倍。
此外,王彩霞等[98]于2015年基于派琴虫ITS基因序列和包纳米虫18S rRNA基因序列建立了贝类派琴虫和包纳米虫的双重LAMP检测法,对两种寄生虫的最低检测限度依次为10拷贝/μL和100拷贝/μL。2013年,Picón-Camacho等[99]基于SSU rDNA序列建立了卵圆鞭毛虫Amyloodinium ocellatum的LAMP检测法,62 ℃、25~30 min水浴条件下即能完成反应,能成功检测到水体和鱼鳃组织中的病原,最低检测浓度为10 fg/反应,显著高于常规的PCR反应(1 pg)。该方法还能检测到单个的分裂前体和滋养体,对于卵圆鞭毛虫病的早期预防和控制具有非常重要的意义。
3 发展现状与前景
LAMP作为一种新型的核酸扩增技术,具有简便、快速、准确、经济等优点,在未来发展前景十分广阔。相比较于目前在水产类病害检测中应用较广且简便、快速、特异性高的ELISA、斑点金免疫渗滤等免疫学诊断技术来说,LAMP能够以指数形式对病原核酸序列大量扩增,在实际应用中能检测出反应管中pg甚至 fg级别的微量核酸,进一步提高了反应的灵敏度。相对于需要高精度的热循环仪器和成像系统的PCR和RT-PCR等技术,LAMP不需要昂贵的仪器和设备,仅通过恒温水浴锅在大约40 min内即可完成反应,甚至在某些野外简陋条件下,利用保温瓶也可粗略完成定性分析。这一优势在基层养殖场的应用中显得尤为明显,特别是在特异性和高灵敏度上的优异表现,使其能够实现对鱼病的早期诊断,不仅能够降低鱼病监测成本,同时还能有效地进行早期控制,避免鱼类病害蔓延带来的经济损失。
然而,就目前的发展现状而言,LAMP还存在诸多的不足。该方法只能检测出是否扩增出DNA而不能判断其是否为特异性扩增;LAMP为链置换合成,靶序列长度不宜过高,最好在300 bp以内,所以不能扩增较长的DNA链。此外,LAMP技术对病原的核酸数据量的需求和对引物的精准度方面提出了更高的要求。另一方面,水浴锅同样需要用电,且其热稳定性没有PCR仪强,可能会导致试验结果稳定性不高,如需在野外条件下运用该方法,如何确保合适的反应温度也是亟待解决的一个问题。
目前,市场已有许多基于LAMP技术的病原检测试剂盒,如WSSV、RSIV、IHNV和KHV等,这些商业化试剂盒的出现也从另一个方面表明了该方法的有效性。此外,LAMP还可将耐药基因作为目的片段,检测耐药病原菌,从而为进一步诊断和控制病害节省时间,尽可能减小疾病的传播范围。对于该技术的发展,其灵敏度过高易引起假阳性结果的弊端无疑是未来改良和优化的一个主要方面,而进一步简化组织样品的处理过程,建立集样品处理、反应和检测3个步骤为一体的简便、经济的一次性套装,可能更利于该技术在生产一线的应用和推广,这也可能成为该技术的主要发展方向。
参考文献:
[1] Notomi T,Okayama H,Masubuchi H,et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2000,28(12):e63.
[2] Poon L L M,Leung C S W,Tashiro M,et al.Rapid detection of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay[J].Clin Chem,2004,50(6):1050-1052.
[3] Dinh D T,Le M T Q,Vuong C D,et al.An updated loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid diagnosis of H5N1 avian influenza viruses[J].Trop Med Health,2011,39(1):3-7.
[4] Guan Hongxing,Li Zhiyong,Yin Xiangping,et al.Rapid detection and differentiation of foot and mouth disease virus serotypes by antigen-capture reverse transcriptase loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Asian J Anim Vet Adv,2013,8(4):647-654.
[5] Zhang Qingli,Shi Chenyin,Huang Jie,et al.Rapid diagnosis of turbot reddish body iridovirus in turbot using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method[J].J Virol Methods,2009,158(1-2):18-23.
[6] Mao X L,Zhou S,Xu D,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of Singapore grouper iridovirus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Appl Microbiol,2008,105(2):389-397.
[7] Gunimaladevi I,Kono T,Venugopal M N,et al.Detection of koi herpesvirus in common carp,Cyprinus carpio L.,by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Fish Dis,2004,27(10):583-589.
[8] Yoshino M,Watari H,Kojima T,et al.Rapid,sensitive and simple detection method for Koi herpesvirus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Microbiol Immunol,2009,53(7):375-383.
[9] He Junqiang,Shi Xiujie,Yu Li,et al.Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for diagnosis of Cyprinid herpesvirus 2[J].J Virol Methods,2013,194(1-2):206-210.
[10] Liang L G,Xie J,Luo D.Development of a rapid cyprinid herpesvirus 2 detection method by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2014,59(4):432-437.
[11] Savan R,Igarashi A,Matsuoka S,et al.Sensitive and rapid detection of Edwardsiellosis in fish by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2004,70(1):621-624.
[12] Yeh H Y,Shoemaker C A,Klesius P H.Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus important bacterial pathogen Edwardsiella ictaluri[J].J Microbiol Methods,2005,63(1):36-44.
[13] Cai S H,Lu Y S,Wu Z H,et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of Vibrio alginolyticus,the causative agent of vibriosis in mariculture fish[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2010,50(5):480-485.
[14] Jones J L,Hara-Kudo Y,Krantz J A,et al.Comparison of molecular detection methods for Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus[J].Food Microbiol,2012,30(1):105-111.
[15] Di Huiling,Ye Lei,Neogi S B,et al.Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay combined with enrichment culture for rapid detection of very low numbers of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood samples[J].Biol Pharm Bull,2015,38(1):82-87.
[16] El-Matbouli M,Soliman H.Rapid diagnosis of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae,the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in salmonid fish by a novel DNA amplification method,loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)[J].Parasitol Res,2005,96(5):277-284.
[17] Jeon C H,Wi S,Song J Y,et al.Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detection of Kudoa septempunctata (Myxozoa:Multivalvulida) in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)[J].Parasitol Res,2014,113(5):1759-1767.
[18] Cai X Q,Xu M J,Wang Y H,et al.Sensitive and rapid detection of Clonorchis sinensis infection in fish by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)[J].Parasitol Res,2010,106(6):1379-1383.
[19] Chen Y,Wen T,Lai D H,et al.Development and evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Clonorchis sinensis from its first intermediate hosts,freshwater snails[J].Parasitology,2013,140(11):1377-1383.
[20] Nagamine K,Hase T,Notomi T.Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers[J].Mol Cell Probes,2002,16(3):223-229.
[21] Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) for rapid detection of viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHS)[J].Vet Microbiol,2006,114(3-4):205-213.
[22] Zhang Min,Jing Hongli,Zhang Lifeng,et al.A loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the detection of members of the genus Ranavirus[J].Arch Virol,2013,158(10):2121-2126.
[23] Suebsing R,Jeon C H,Oh M J,et al.Reverse transcriptase loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus in Oncorhynchus keta[J].Dis Aquat Organ,2011,94(1):1-8.
[24] Soliman H,Saleh M,El-Matbouli M.Detection of fish pathogens by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique[M]//Cunha M V,Inácio J.Veterinary Infection Biology:Molecular Diagnostics and High-Throughput Strategies.New York:Humana Press,2015:163-173.
[25] Zhang Qingli,Standish I,Winters A D,et al.Development and evaluation of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the detection of the fathead minnow nidovirus[J].J Virol Methods,2014,202:39-45.
[26] Xie Guosi,Huang Jie,Zhang Qingli,et al.Specific and rapid diagnosis of Edwardsiella tarda by a novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeting the upstream region of hlyb gene[J].J Aquat Anim Health,2013,25(2):110-118.
[27] Hwang J,Suh S S,Park M,et al.Detection of coat protein gene of nervous necrosis virus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Asian Pac J Trop Med,2016,9(3):235-240.
[28] Caipang C M A,Haraguchi I,Ohira T,et al.Rapid detection of a fish iridovirus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)[J].J Virol Methods,2004,121(2):155-161.
[29] 蔡怡,周前进,陈炯.环介导等温扩增联合横向侧流试纸(LAMP-LFD)对嗜水气单胞菌快速检测方法的建立[J].中国兽医学报,2016,36(2):256-264.
[30] Ding W C,Chen J,Shi Y H,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J].Arch Virol,2010,155(3):385-389.
[31] Suebsing R,Kampeera J,Tookdee B,et al.Evaluation of colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for visual detection of Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus iniae in tilapia[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2013,57(4):317-324.
[32] 何琳,徐海圣,王美珍,等. LAMP快速检测对虾IHHNV的方法与应用[J].病毒学报,2010,26(6):490-495.
[33] 王子浩.致病性维氏气单胞菌LAMP方法的建立与应用[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2013.
[34] 何琳.环介导等温扩增技术快速检测水产动物病原的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2012.
[35] 黄灿华,陈棣华,吴清江.对虾病毒病害研究的新进展[J].海洋湖沼通报,1998(4):69-81.
[36] Kono T,Savan R,Sakai M,et al.Detection of white spot syndrome virus in shrimp by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Virol Methods,2004,115(1):59-65.
[37] 冯华,张改平,郭军庆,等.对虾白斑综合征病毒LAMP检测方法的建立[J].中国兽医科学,2011,41(7):707-711.
[38] Chou P H,Lin Yuchan,Teng Pinghua,et al.Real-time target-specific detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for white spot syndrome virus using fluorescence energy transfer-based probes[J].J Virol Methods,2011,173(1):67-74.
[39] 方勤,朱作言.水生呼肠孤病毒研究进展[J].中国病毒学,2003,18(1):82-86.
[40] Zhang Qingli,Yan Yi,Shen Jinyu,et al.Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of grass carp reovirus[J].J Virol Methods,2013,187(2):384-389.
[41] Zeng W W,Wang Q,Wang Y Y,et al.A one-step molecular biology method for simple and rapid detection of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella reovirus (GCRV) HZ08 strain[J].J Fish Biol,2013,82(5):1545-1555.
[42] Chen Jigang,Xiong Juan,Cui Bojing,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of mud crab Scylla serrata reovirus by a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay[J].J Virol Methods,2011,178(1-2):153-160.
[43] Ma Y,Dai T,Serwadda A,et al.Detecting a novel Eriocheir sinensis reovirus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2016,63(5):363-368.
[44] Suebsing R,Pradeep P J,Jitrakorn S,et al.Detection of natural infection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus in farmed tilapia by hydroxynapthol blue-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay[J].J Appl Microbiol,2016,121(1):55-67.
[45] 刘星星,耿毅,汪开毓,等.大鲵蛙病毒LAMP检测方法的建立[J].中国兽医学报,2015,35(4):558-564.
[46] Gunimaladevi I,Kono T,Lapatra S E,et al.A loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J].Arch Virol,2005,150(5):899-909.
[47] Shivappa R B,Savan R,Kono T,et al.Detection of spring viraemia of carp virus (SVCV) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in koi carp,Cyprinus carpio L.[J].J Fish Dis,2008,31(4):249-258.
[48] Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.An inexpensive and rapid diagnostic method of Koi herpesvirus (KHV) infection by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Virol J,2005,2:83.
[49] Zhang Hui,Zeng Lingbing,Fan Yuding,et al.A loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of cyprinid herpesvirus 2 in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio)[J].Sci World J,2014,2014:716413.
[50] Zhu Min,Liu Bo,Cao Guangli,et al.Identification and rapid diagnosis of the pathogen responsible for haemorrhagic disease of the gill of Allogynogenetic crucian carp[J].J Virol Methods,2015,219:67-74.
[51] Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.Immunocapture and direct binding loop mediated isothermal amplification simplify molecular diagnosis of Cyprinid herpesvirus-3[J].J Virol Methods,2009,162(1-2):91-95.
[52] Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.Loop mediated isothermal amplification combined with nucleic acid lateral flow strip for diagnosis of cyprinid herpes virus-3[J].Mol Cell Probes,2010,24(1):38-43.
[53] Li Qiong,Yue Zhiqin,Liu Hong,et al.Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of lymphocystis disease virus[J].J Virol Methods,2010,163(2):378-384.
[54] Valverde E J,Cano I,Castro D,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of lymphocystis disease virus genotype VII by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Food Environ Virol,2017,9(1):114-122.
[55] Pillai D,Bonami J R,Sri Widada J.Rapid detection of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus (XSV),the pathogenic agents of white tail disease of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man),by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Fish Dis,2006,29(5):275-283.
[56] Sung C H,Lu J K.Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and sensitive detection of nervous necrosis virus in groupers[J].J Virol Methods,2009,159(2):206-210.
[57] Suebsing R,Oh M J,Kim J H.Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting nervous necrosis virus in olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus[J].J Microbiol Biotechnol,2012,22(7):1021-1028.
[58] Mekata T,Satoh J,Inada M,et al.Development of simple,rapid and sensitive detection assay for grouper nervous necrosis virus using real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Fish Dis,2015,38(10):873-879.
[59] Xu Haidong,Feng Juan,Guo Zhixun,et al.Detection of red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Virol Methods,2010,163(1):123-128.
[60] 刘淼,徐黎明,赵景壮,等.虹鳟传染性胰脏坏死病毒的分离鉴定及聚类分析[J].大连海洋大学学报,2017,32(1):56-61.
[61] Soliman H,Midtlyng P J,El-Matbouli M.Sensitive and rapid detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus by reverse transcription loop mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Virol Methods,2009,158(1-2):77-83.
[62] Suebsing R,Oh M J,Kim J H.Evaluation of rapid and sensitive reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta)[J].J Vet Diagn Invest,2011,23(4):704-709.
[63] Suebsing R,Kim J H,Kim S R,et al.Detection of viruses in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Korea by RT-LAMP assay[J].J Microbiol,2011,49(5):741-746.
[64] Andrade T P D,Lightner D V.Development of a method for the detection of infectious myonecrosis virus by reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification and nucleic acid lateral flow hybrid assay[J].J Fish Dis,2009,32(11):911-924.
[65] Sun Zhaofeng,Hu Chaoqun,Ren Chunhua,et al.Sensitive and rapid detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in shrimps by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Virol Methods,2006,131(1):41-46.
[66] Arunrut N,Prombun P,Saksmerprome V,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J].J Virol Methods,2011,171(1):21-25.
[67] 丁文超,胡健饶,史雨红,等. 环介导恒温扩增技术快速检测溶藻弧菌[J].分子细胞生物学报,2009,42(1):70-76.
[68] Plaon S,Longyant S,Sithigorngul P,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio alginolyticus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick targeted to the rpoX gene[J].J Aquat Anim Health,2015,27(3):156-163.
[69] Yamazaki W,Ishibashi M,Kawahara R,et al.Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for sensitive and rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J].BMC Microbiol,2008,8:163.
[70] Zeng Jing,Wei Haiyan,Zhang Lei,et al.Rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in raw oysters using immunomagnetic separation combined with loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2014,174:123-128.
[71] Han Feifei,Ge Beilei.Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Vibrio vulnificus in raw oysters[J].Foodborne Pathog Dis,2008,5(3):311-320.
[72] Han H J,Jung S J,Oh M J,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of Streptococcus iniae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)[J].J Fish Dis,2011,34(5):395-398.
[73] Wang Yi,Li Dongxun,Wang Yan,et al.Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus by multiple endonuclease restriction real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique[J].Molecules,2016,21(1):111.
[74] Zhou Shun,Gao Zhixin,Zhang Min,et al.Development of a quadruplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for field detection of four Vibrio species associated with fish disease[J].Springerplus,2016,5(1):1104.
[75] Cao Y T,Wu Z H,Jian J C,et al.Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of Vibrio harveyi in cultured marine shellfish[J].Lett Appl Microbiol,2010,51(1):24-29.
[76] 高志鑫,张敏,王西西,等.大菱鲆弧菌LAMP快速检测方法的建立与初步应用[J].青岛农业大学学报:自然科学版,2015,32(4):284-288.
[77] 杜明洋,叶仕根,刘娟,等.水产动物病原拮抗微生物及其应用研究进展[J].大连海洋大学学报,2017,32(6):753-758.
[78] Cai Shuanghu,Wang Bei,Lu Yishan,et al.Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of Streptococcus iniae,the causative agent of streptococcicosis in fish[J].J Basic Microbiol,2012,52(2):116-122.
[79] 郑磊,樊海平,吴斌,等.罗非鱼无乳链球菌LAMP快速检测方法的建立[J].福州大学学报:自然科学版,2015,43(4):572-576.
[80] 王瑞娜,周前进,陈炯.环介导等温扩增联合横向流动试纸条可视化检测海豚链球菌方法的建立[J].农业生物技术学报,2014,22(12):1584-1594.
[81] 姚学良,徐晓丽,李贺密,等.红尾皇冠鱼无乳链球菌病LAMP检测方法的建立与应用[J].大连海洋大学学报,2014,29(6):561-565.
[82] 程天印,刘洵,常小斌.嗜水气单胞菌LAMP检测方法的建立及应用[J].中国兽医科学,2007,37(12):1013-1016.
[83] 匡燕云.环介导等温扩增技术检测嗜水气单胞菌方法的建立[D].南昌:南昌大学,2007.
[84] 李嘉彬,马艳平,柯浩,等.嗜水气单胞菌与温和气单胞菌的LAMP检测方法的建立[J].南方水产科学,2014,10(5):8-16.
[85] Itano T,Kawakami H,Kono T,et al.Detection of fish nocardiosis by loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Appl Microbiol,2006,100(6):1381-1387.
[86] Yeh H Y,Shoemaker C A,Klesius P H.Sensitive and rapid detection of Flavobacterium columnare in channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method[J].J Appl Microbiol,2006,100(5):919-925.
[87] Fujiwara-Nagata E,Eguchi M.Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid and simple detection of Flavobacterium psychrophilum[J].J Fish Dis,2009,32(10):873-881.
[88] Saleh M,Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Renibacterium salmoninarum,the causative agent of bacterial kidney disease[J].Dis Aquat Organ,2008,81(2):143-151.
[89] Gahlawat S K,Ellis A E,Collet B.A sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for detection of Renibacterium salmoninarum,causative agent of bacterial kidney disease in salmonids[J].J Fish Dis,2009,32(6):491-497.
[90] Saleh M,Soliman H,El-Matbouli M.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification as an emerging technology for detection of Yersinia ruckeri the causative agent of enteric red mouth disease in fish[J].BMC Vet Res,2008,4:31.
[91] Caipang C M A,Kulkarni A,Brinchmann M F,et al.Detection of Francisella piscicida in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) by the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) reaction[J].Vet J,2010,184(3):357-361.
[92] Mao Zhijuan,Qiu Yangyu,Zheng Lei,et al.Development of a visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas putida of the large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea)[J].J Microbiol Methods,2012,89(3):179-184.
[93] Tsai M A,Wang P C,Yoshida T,et al.Development of a sensitive and specific LAMP PCR assay for detection of fish pathogen Lactococcus garvieae[J].Dis Aquat Organ,2013,102(3):225-235.
[94] El-Matbouli M,Soliman H.Development of a rapid assay for the diagnosis of Myxobolus cerebralis in fish and oligochaetes using loop-mediated isothermal amplification[J].J Fish Dis,2005,28(9):549-557.
[95] Sugita-Konishi Y,Fukuda Y,Mori K I,et al.New validated rapid screening methods for identifying Kudoa septempunctata in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)[J].Jpn J Infect Dis,2015,68(2):145-147.
[96] 杨秋林,许丽芳,张愉快,等.环介导等温扩增技术检测日本血吸虫尾蚴的实验研究[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2008,20(3):209-211.
[97] 邓鹏程.LAMP快速检测日本血吸虫感染性钉螺、卡氏肺孢子虫及恶性疟原虫的研究[D].衡阳:南华大学,2013.
[98] 王彩霞,冯春燕,王巧黎,等.同时检测贝类派琴虫和包纳米虫的双重LAMP方法的建立[J].中国畜牧兽医,2015,42(8):1935-1942.
[99] Picón-Camacho S M,Thompson W P,Blaylock R B,et al.Development of a rapid assay to detect the dinoflagellate Amyloodinium ocellatum using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)[J].Vet Parasitol,2013,196(3-4):265-271.